初识MCP
MCP(Model Context Protocol),是一个开发的协议,标准化了应用程序如何为大模型提供上下文。MCP提供了一个标准的为LLM提供数据、工具的方式,使用MCP会更容易的构建Agent或者是基于LLM的复杂工作流。
架构
MCP是CS结构,一个MCP host应用可以链接多个MCP servers。 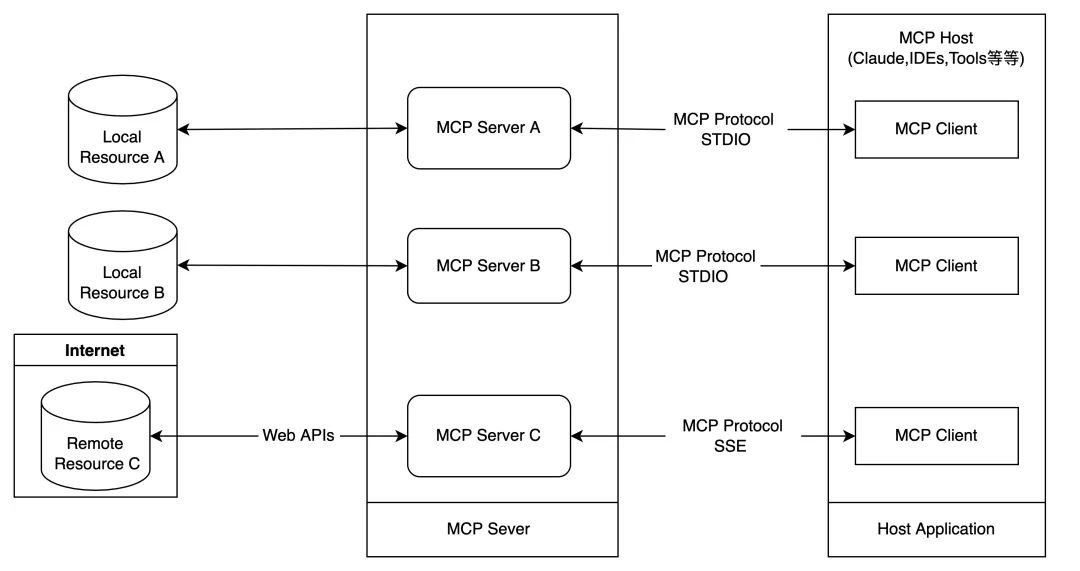
- MCP Host:需要通过MCP获得数据的程序,例如Claude Desktop, IDEs或者一些AI工具等
- MCP Client: MCP协议客户端,和MCP Server是一对一支持的。
- MCP Server:需要通过MCP暴露一些特殊的能力的轻应用。根据MCP协议定义,Server可以提供三种类型的标准能力,Resources、Tools、Prompts,每个Server可同时提供者三种类型能力或其中一种。
- Resources:资源,类似于文件数据读取,可以是文件资源或是API响应返回的内容。
- Tools:工具,第三方服务、功能函数,通过此可控制LLM可调用哪些函数。
- Prompts:提示词,为用户预先定义好的完成特定任务的模板
- Local Data Resources:MCP Server可以安全访问的本地的文件、数据库、服务等。
- Remote Service:MCP Server可通过网络(如 API)连接的外部系统。
MCP的服务示意图: 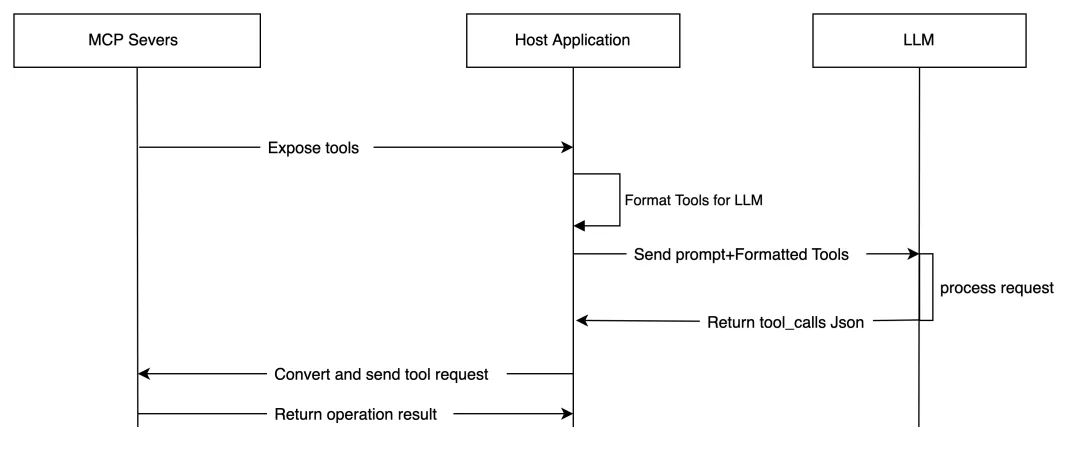
MCP Servers通过MCP Protocol向Host Application提供一些功能列表(例如提供一个工具列表),然后Host Application会将这个列表格式化成一个LLM能读懂的格式。 Host Application可以利用这个功能列表向LLM发送一些需要大模型处理的请求(这就是prompt),LLM会根据这次的prompt返回一个tool_calls的json字符串。当Host Applicaiton接受到这个tool_calls后,就会调用对应的MCP server工具返回对应的结果了。
借助Claude Desktop 使用MCP
借助Claude桌面客户端,肯定要先安装一个,这个安装就跳过了。我们配置一个文件系统的MCP Server。 
然后选择Developer下的Edit Config、 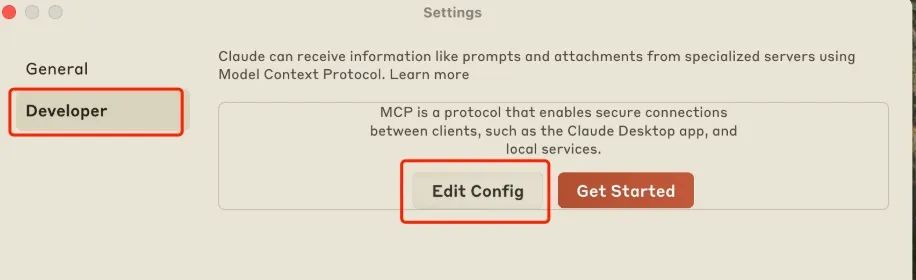
打开claude_desktop_config.json,完成文件系统的MCP Server配置。(配置中username需要替换成自己自己电脑的用户名,同时也需要本地安装node.js的环境。)
{
"mcpServers": {
"filesystem": {
"command": "npx",
"args": [
"-y",
"@modelcontextprotocol/server-filesystem",
"/Users/username/Desktop",
"/Users/username/Downloads"
]
}
}
}配置完成后,重启Cluade客户端。就可以试一下了。
点击锤子的icon就可以看到MCP Server提供的工具了。

下面输入如下的prompt可以试一下
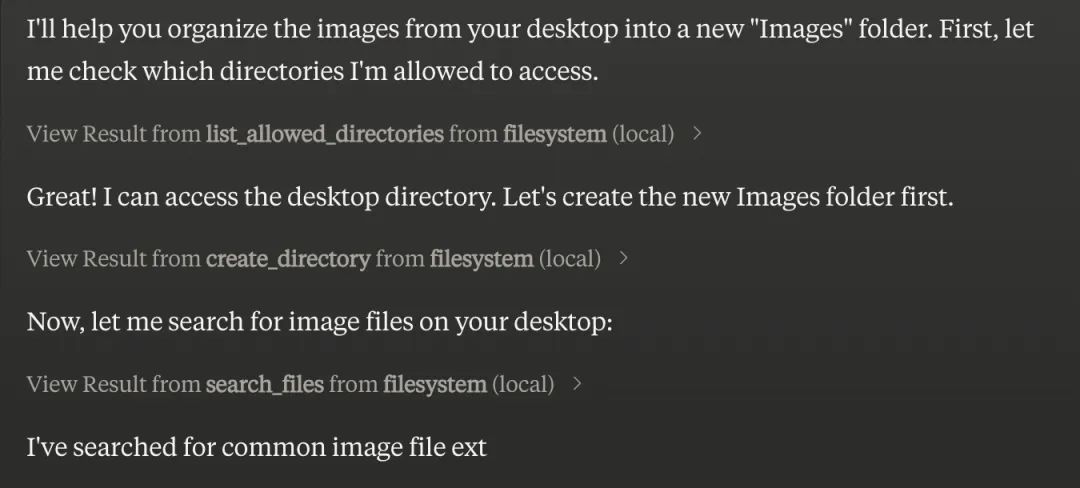
Can you take all the images on my desktop and move them to a new folder called “Images”?
LLM的反馈和文件系统MCP server执行的时候,还有几次权限的提醒,记得允许。
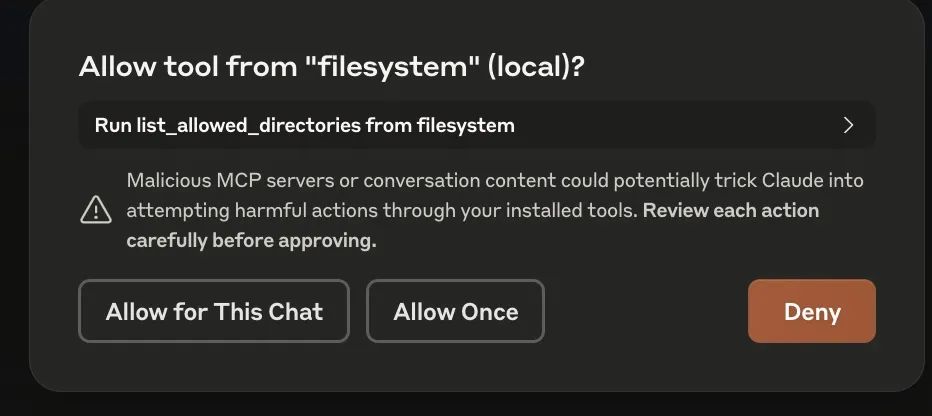
然后你就可以看到LLM、MCPServer开始工作了。
MCP Server开发的入门教程(python和pip)
使用python技术栈开发的简单mcp server
需要安装
MCP server的需要使用python-sdk,python需要 3.10,安装如下
pip install mcp
PS: MCP官方使用的是uv包管理工具,我平时使用pip比较多,所以文中以pip为主。因为mcp的一些依赖包版本并不是最新的,所以最好弄一个干净的环境。 开发一个MCP Server需要的调试客户端,MCP inspector提供了这个功能
npx @modelcontextprotocol/inspector <command> <arg1> <arg2>
其中command我们要是使用python写的Server,就应该python。<arg1> <arg2>是可选参数。 启动后
开发一个demo的MCP Server
MCP Server:需要通过MCP暴露一些特殊的能力的轻应用。根据MCP协议定义,Server可以提供三种类型的标准能力,Resources、Tools、Prompts,每个Server可同时提供者三种类型能力或其中一种。
- Resources:资源,类似于文件数据读取,可以是文件资源或是API响应返回的内容。
- Tools:工具,第三方服务、功能函数,通过此可控制LLM可调用哪些函数。
- Prompts:提示词,为用户预先定义好的完成特定任务的模板
下面我们利用python-sdk,对如上三种类型的能力进行一下演示。
Prompts
首先我们以prompt开始,通过handle_list_promopts列出可用的提示词模板,handle_get_prompt是根据名称获取特定的提示模板。
@server.list_prompts()
async def handle_list_prompts() -> list[types.Prompt]:
"""
提示模版定义
"""
return [
types.Prompt(
name="example-prompt",
description="An example prompt template",
arguments=[
types.PromptArgument(
name="arg1",
description="Example argument",
required=True
)
]
)
]
@server.get_prompt()
async def handle_get_prompt(
name: str,
arguments: dict[str, str] | None
) -> types.GetPromptResult:
"""
提示模板处理
"""
if name != "example-prompt":
raise ValueError(f"Unknown prompt: {name}")
return types.GetPromptResult(
description="Example prompt",
messages=[
types.PromptMessage(
role="user",
content=types.TextContent(
type="text",
text="Example prompt text"
)
)
]
)
Resources
资源管理功能的代码list_resources列出可用的资源,返回一个资源列表。read_resource读取指定 URI 的资源内容。SAMPLE_RESOURCES是为了测试建立的一个demo
@server.list_resources()
async def list_resources() -> list[types.Resource]:
"""
资源定义
"""
test='test'
return [
types.Resource(
uri=AnyUrl(f"file:///{test}.txt"),
name=test,
description=f"A sample text resource named {test}",
mimeType="text/plain",
)
# for name in SAMPLE_RESOURCES.keys()
]
SAMPLE_RESOURCES={'test':'this demo is a mcp server!'}
@server.read_resource()
async def read_resource(uri: AnyUrl) -> str | bytes:
assert uri.path is not None
print(uri.path)
name = uri.path.replace(".txt", "").lstrip("/")
# print(name)
if name not in SAMPLE_RESOURCES:
raise ValueError(f"Unknown resource: {uri}")
return SAMPLE_RESOURCES[name]
Tools
工具定义和调用,handle_list_tools定义可用的工具,使用 JSON Schema 验证工具参数。handle_call_tool处理工具调用,根据工具名称和参数执行相应的操作。 @server.list_tools() async def handle_list_tools() -> list[types.Tool]: """ 工具定义. 每个工具都使用JSON Schema验证指定其参数. """ return [ types.Tool( name="demo-tool", description="Get data tool for a param", inputSchema={ "type": "object", "properties": { "param": { "type": "string", "description": "url", }, }, "required": ["param"], }, ) ] @server.call_tool() async def handle_call_tool( name: str, arguments: dict | None ) -> list[Any]: logging.info(name) """ 处理工具调用 """ if not arguments: raise ValueError("Missing arguments") if name == "demo-tool": param = arguments.get("param") if not param: raise ValueError("Missing state parameter") param = param.upper() return [ types.TextContent( type="text", text=f"text:{param}" ) ] else: raise ValueError(f"Unknown tool: {name}")
inspector
如下已经写好了一个MCP Server,可以启动MCP inspector进行调试,在Server代码所在目录输入
npx @modelcontextprotocal/inspector
启动后,得到如下截图按照图中显示,访问http://localhost:5273,按照前面说的,transport type选择STDIO,command输入python,Arguments输入server.py(上面的demo代码保存到了server.py的文件里面),点击connect。在图上通过各个类型进入对应的Server服务的调用,在Resources中点击List Resource,就可以列出全部的resource,点击对应的resource,就可以看到具体resource的内容。
这样就可以和我们已经开发好的MCP Server进行交互了。
如何配置到Claude desktop中
按照刚才在inspector中的命令配置,将这个MCP Server配置到Claude中。点击Claude desktop的setting,选择developer的tab后,点击edit config,跳转到claude_desktop_config.json。
目前我已经安装了两个MCP Server,配置如下,一个是文件整理,一个是playwright(要通过npx安装playwright的MCP Server。
{
"mcpServers": {
"filesystem": {
"command": "npx",
"args": [
"-y",
"@modelcontextprotocol/server-filesystem",
"/Users/crisschan/Desktop",
"/Users/crisschan/Downloads"
]
},
"playwright": {
"command": "npx",
"args": ["-y",
"@executeautomation/playwright-mcp-server"]
}
}
}
将我们自己的demo服务按照这个格式配置好,然后保存后重启Claude desktop。
{
"mcpServers": {
,
"demo": {
"command": "/opt/anaconda3/bin/python3",
"args": ["/Users/workspace/pyspace/try_mcp/server.py"]
}
}
}
其中在配置的时候,command必须是对应版本的python绝对地址,args中的server.py代码位置也是一样,要使用绝对地址。
© 版权声明
文章版权归 AI分享圈 所有,未经允许请勿转载。
相关文章

暂无评论...