引言
DashInfer-VLM是一个针对于视觉多模态大模型VLM的推理架构,特别优化了Qwen VL模型的推理加速,DashInfer-VLM和其他的VLM的推理加速框架最大的区别是, 它把VIT部分和LLM部分进行了分离,并且VIT和LLM的运行是并行运行,不互相干扰。
这样做的特点是,在VLM中的图片,视频预处理,以及VIT的特征抽取部分,不会打断LLM的生成,也可以成为VIT/LLM分离的架构,是目前开源社区首个使用该架构的VLM 服务框架。
在多卡部署下,它在每张卡上都有一个ViT的处理单元,这样在视频,多图的场景下,有非常显著的性能优势。
另外,ViT部分,它支持了内存缓存,这样在多轮对话下,不需要重复计算ViT。
下面是它的架构图, 以及按照4卡部分72B的进行的配置。
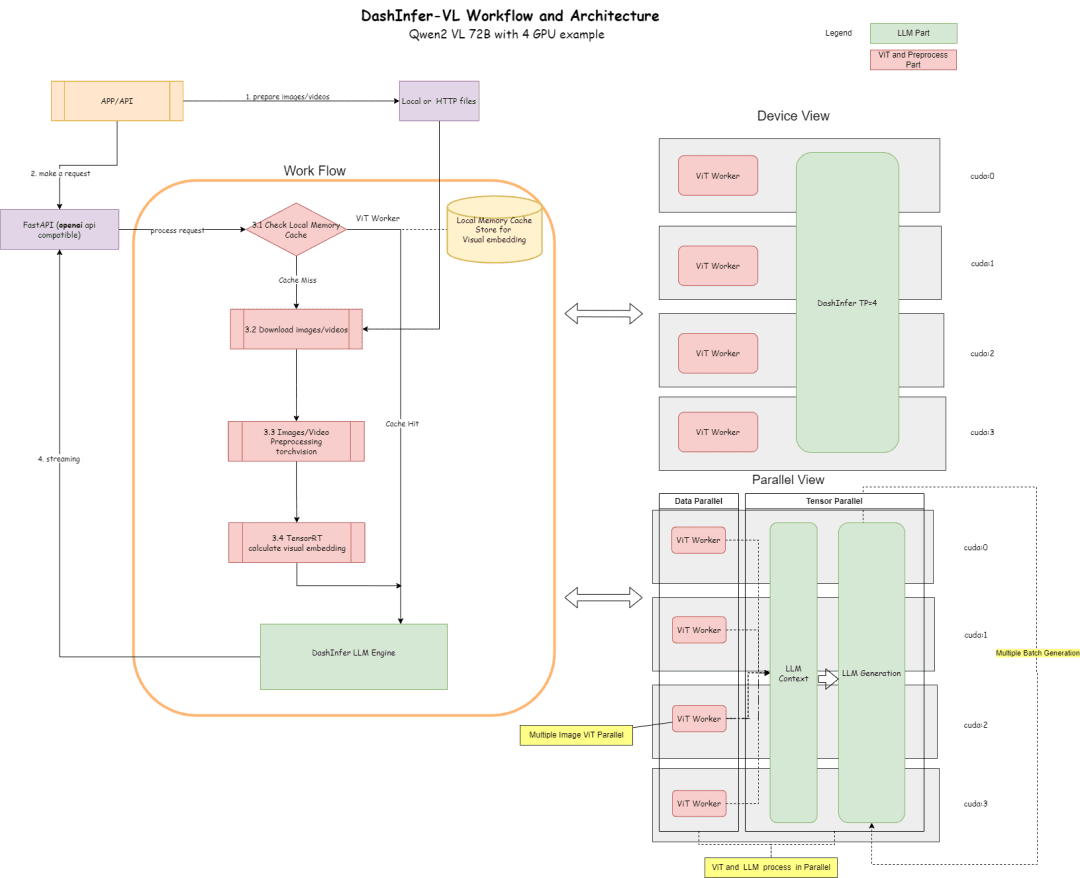
架构图描述了流程和架构:
- 在ViT部分,可以使用很多推理引起进行推理,比如TensorRT 或者 onnxruntime(在框架内会对模型的ViT部分进行onnx模型导出,)目前框架内默认支持了TensorRT。
- 在LLM部分,使用DashInfer进行推理。
- Cache部分,支持ViT结果 Memory Cache, LLM部分Prerfix Cache, LLM 部分多模态 Prefix Cache(默认未开启)
代码地址:
https://github.com/modelscope/dash-infer
文档地址:
https://dashinfer.readthedocs.io/en/latest/vlm/vlm_offline_inference_en.html
最佳实践
在魔搭社区免费GPU算力上体验DashInfer:
首先是dashinfer-vlm和TensorRT的安装。 # 首先安装所需的 package import os # 下载并安装 dashinfer 2.0.0rc2 版本 # 如果需要,可以使用 wget 下载并解压 TensorRT 包 # pip 安装 dashinfer 2.0.0rc2 #!pip install https://github.com/modelscope/dash-infer/releases/download/v2.0.0-rc2/dashinfer-2.0.0rc2-cp310-cp310-manylinux_2_17_x86_64.manylinux2014_x86_64.whl #!wget https://modelscope.oss-cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com/releases/TensorRT-10.6.0.26.Linux.x86_64-gnu.cuda-12.6.tar.gz #!tar -xvzf TensorRT-10.6.0.26.Linux.x86_64-gnu.cuda-12.6.tar.gz # 下载到本地并替换为 modelscope 对应的 URL # 安装 dashinfer,因 package 较大,推荐下载到本地后安装 #!wget https://modelscope.oss-cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com/releases/dashinfer-2.0.0rc3-cp310-cp310-manylinux_2_17_x86_64.manylinux2014_x86_64.whl #!pip install ./dashinfer-2.0.0rc3-cp310-cp310-manylinux_2_17_x86_64.manylinux2014_x86_64.whl # 安装 dashinfer vlm #!pip install dashinfer-vlm # 安装 OpenAI 客户端 #!pip install openai==1.56.2 # 安装 TensorRT 的 Python 包,从下载的包中打开安装 #!pip install TensorRT-10.6.0.26/python/tensorrt-10.6.0-cp310-none-linux_x86_64.whl
TensorRT 需要进行环境变量配置:
import os
# 获取 TensorRT 运行时库的路径
trt_runtime_path = os.getcwd() + "/TensorRT-10.6.0.26/lib/"
# 获取当前的 LD_LIBRARY_PATH 环境变量值
current_ld_library_path = os.environ.get('LD_LIBRARY_PATH', '')
# 将新路径添加到现有值中
if current_ld_library_path:
# 如果 LD
环境安装完成, 启动 dashinfer vlm对模型进行推理,并且形成一个 openai兼容的server, 模型可以换成 7B, 72B等。
默认会使用环境里面所有的GPU显存
!dashinfer_vlm_serve --model qwen/Qwen2-VL-2B-Instruct --port 8000 --host 127.0.0.1
这个过程会初始化DashInfer,以及ViT用的外部引擎(这里是TensorRT),并且起一个openai的service。
看到这些日志表示TRT初始化成功:
看到这些日志,表示DashInfer初始化成功:

看到这些日志,表示openai服务初始化成功:

到这里全部初始化成功, 可以打开另一个notebook进行client和benchmark
Notebook地址:https://modelscope.cn/notebook/share/ipynb/6ea987c5/vl-start-server.ipynb
图片理解Demo
展示一个多张图片的图片理解的demo:
# Install the required OpenAI client version
!pip install openai==1.56.2 # VL support requires a recent OpenAI client.
from openai import OpenAI
# Initialize the OpenAI client
client = OpenAI(
base_url="http://localhost:8000/v1",
api_key="EMPTY"
)
# Prepare the API call for a chat completion
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model="model",
messages=[
{
"role": "user",
"content": [
{"type": "text", "text": "Are these images different?"},
{
"type": "image_url",
"image_url": {
"url": "https://farm4.staticflickr.com/3075/3168662394_7d7103de7d_z_d.jpg",
}
},
{
"type": "image_url",
"image_url": {
"url": "https://farm2.staticflickr.com/1533/26541536141_41abe98db3_z_d.jpg",
}
},
],
}
],
stream=True,
max_completion_tokens=1024,
temperature=0.1,
)
# Process the streamed response
full_response = ""
for chunk in response:
# Append the delta content to the full response
full_response += chunk.choices[0].delta.content
print(".", end="") # Print a dot for each chunk received
# Print the full response
print(f"\nImage: Full Response:\n{full_response}")
视频理解demo
由于openai没有定义标准的视频接口,本文提供了一个video_url的type, 会自动进行视频下载,抽帧,分析的工作。
# video example
!pip install openai==1.56.2 # Ensure the OpenAI client supports video link features.
from openai import OpenAI
# Initialize the OpenAI client
client = OpenAI(
base_url="http://localhost:8000/v1",
api_key="EMPTY"
)
# Create a chat completion request with a video URL
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model="model",
messages=[
{
"role": "user",
"content": [
{
"type": "text",
"text": "Generate a compelling description that I can upload along with the video."
},
{
"type": "video_url",
"video_url": {
"url": "https://cloud.video.taobao.com/vod/JCM2awgFE2C2vsACpDESXZ3h5_iQ5yCZCypmjtEs2Ck.mp4",
"fps": 2
}
}
]
}
],
max_completion_tokens=1024,
top_p=0.5,
temperature=0.1,
frequency_penalty=1.05,
stream=True,
)
# Process the streaming response
full_response = ""
for chunk in response:
# Append the delta content from the chunk to the full response
full_response += chunk.choices[0].delta.content
print(".", end="") # Indicate progress with dots
# Print the complete response
print(f"\nFull Response: \n{full_response}")
benchmark
使用上面的图片理解example,简单的做一个多并发的测试进行吞吐测试。
# benchmark!pip install openai==1.56.2
import time
import concurrent.futures
from openai import OpenAI
# 初始化 OpenAI 客户端
client = OpenAI(
base_url="http://localhost:8000/v1",
api_key="EMPTY"
)
# 请求参数
model = "model"
messages = [
{
"role": "user",
"content": [
{"type": "text", "text": "Are these images different?"},
{
"type": "image_url",
"image_url": {
"url": "https://farm4.staticflickr.com/3075/3168662394_7d7103de7d_z_d.jpg",
}
},
{
"type": "image_url",
"image_url": {
"url": "https://farm2.staticflickr.com/1533/26541536141_41abe98db3_z_d.jpg",
}
},
],
}
]
# 并发请求函数
def send_request():
start_time = time.time()
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model=model,
messages=messages,
stream=False,
max_completion_tokens=1024,
temperature=0.1,
)
end_time = time.time()
latency = end_time - start_time
return latency
# 基准测试函数
def benchmark(num_requests, num_workers):
latencies = []
start_time = time.time()
with concurrent.futures.ThreadPoolExecutor(max_workers=num_workers) as executor:
futures = [executor.submit(send_request) for _ in range(num_requests)]
for future in concurrent.futures.as_completed(futures):
latencies.append(future.result())
end_time = time.time()
total_time = end_time - start_time
qps = num_requests / total_time
average_latency = sum(latencies) / len(latencies)
throughput = num_requests * 1024 / total_time # 假设每个请求的响应大小为 1024 字节
print(f"Total Time: {total_time:.2f} seconds")
print(f"QPS: {qps:.2f}")
print(f"Average Latency: {average_latency:.2f} seconds")
# 主程序入口
if __name__ == "__main__":
num_requests = 100 # 总请求数
num_workers = 10 # 并发工作线程数
benchmark(num_requests, num_workers)
测试结果:
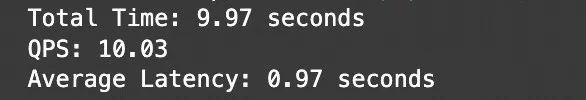
Notebook地址:https://modelscope.cn/notebook/share/ipynb/5560603a/vl-test-and-benchmark.ipynb
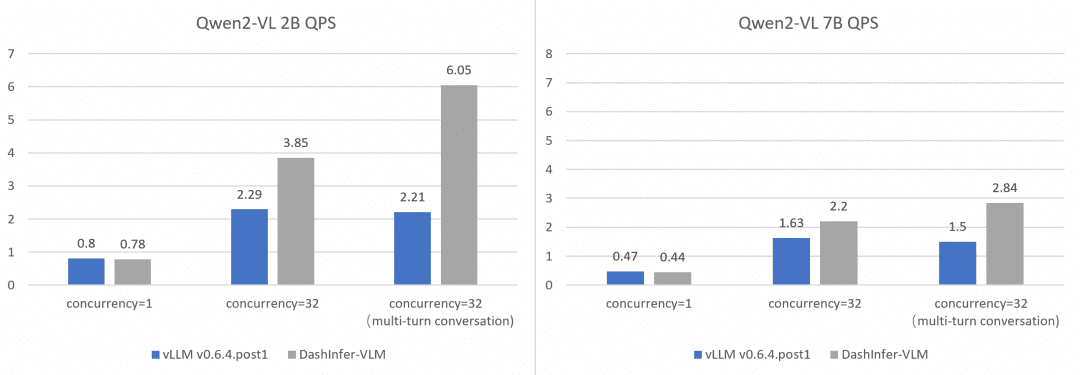
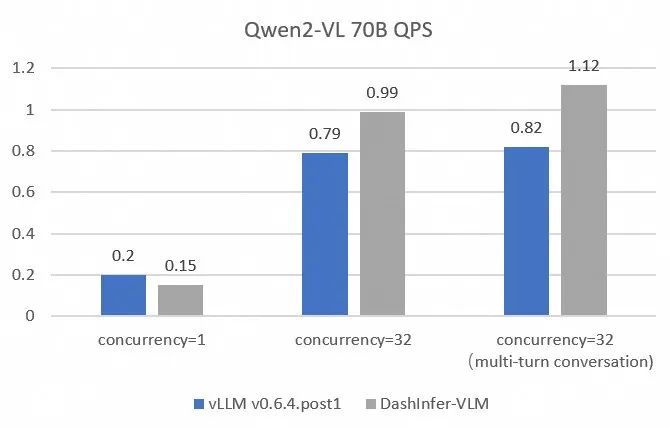
全面和vLLM的性能对比:
为了更加全面和准确的对比和vLLM的性能,我们在不同size的模型上使用 OpenGVLab/InternVL-Chat-V1-2-SFT-Data 进行了单并发,多并发,以及多轮对话的benchmark,详细的复现脚本见链接, 结果如下:
可以看到DashInfer在各个情况下均有一定的性能优势,尤其在多轮对话中优势更加明显。
© 版权声明
文章版权归 AI分享圈 所有,未经允许请勿转载。
相关文章

暂无评论...