cognee: фреймворк с открытым исходным кодом для построения RAG на основе графа знаний, обучение по основным подсказкам
Общее введение
Cognee - это надежное решение на уровне данных, предназначенное для приложений ИИ и агентов ИИ. Предназначен для загрузки и построения контекстов LLM (Large Language Model) для создания точных и интерпретируемых решений ИИ с помощью графов знаний и векторных хранилищ. Фреймворк обеспечивает экономию средств, интерпретируемость и настраиваемое пользователем управление, что делает его пригодным для использования в исследовательских и образовательных целях. На официальном сайте представлены вводные учебные пособия, концептуальные обзоры, учебные материалы и информация о сопутствующих исследованиях.
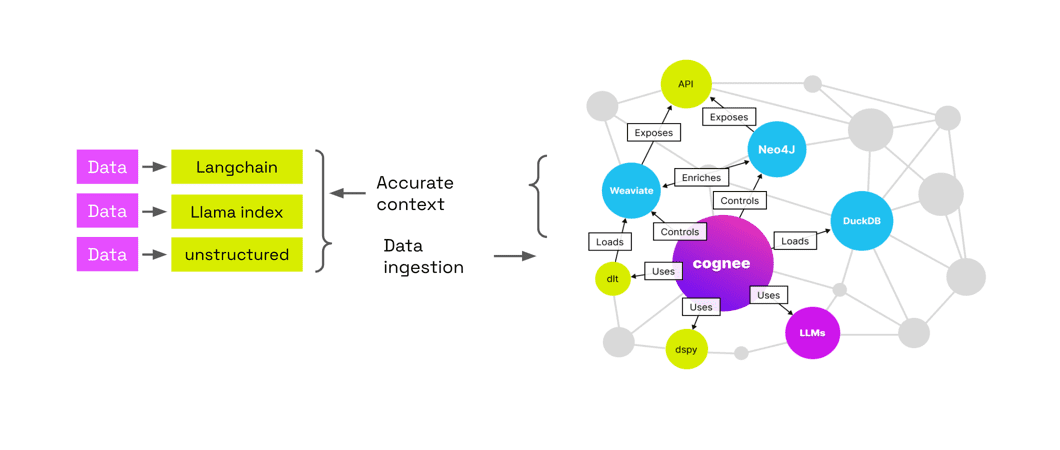
Самая сильная сторона cognee - это предоставление данных, их автоматическая обработка, построение графа знаний и повторное соединение графов связанных тем, чтобы помочь вам лучше выявить связи в данных, а также RAG Обеспечивает максимальную интерпретируемость, когда речь идет о LLM.
1. добавление данных, автоматическая идентификация и обработка данных на основе LLM, извлечение в Knowledge Graph и возможность хранения weaviate векторная база данных 2. Преимущества: экономия денег, интерпретируемость - графическая визуализация данных, управляемость - интеграция в код и т.д.
Список функций
- Трубопроводы ECL: Обеспечивает извлечение, познание и загрузку данных, поддерживает взаимосвязь и поиск исторических данных.
- Поддержка нескольких баз данных: Поддержка PostgreSQL, Weaviate, Qdrant, Neo4j, Milvus и других баз данных.
- Уменьшение галлюцинаций: Уменьшение фантомных явлений в приложениях искусственного интеллекта путем оптимизации конструкции трубопроводов.
- Дружелюбный к разработчикам: Предоставьте подробную документацию и примеры, чтобы снизить порог для разработчиков.
- масштабируемость: Модульная конструкция для легкого расширения и настройки.
Использование помощи
Процесс установки
- Установка с помощью pip::
pip install cogneeИли установите специальную поддержку баз данных:
pip install 'cognee[<database>]'Например, установите поддержку PostgreSQL и Neo4j:
pip install 'cognee[postgres, neo4j]' - Инсталляция с использованием поэзии::
poetry add cogneeИли установите специальную поддержку баз данных:
poetry add cognee -E <database>Например, установите поддержку PostgreSQL и Neo4j:
poetry add cognee -E postgres -E neo4j
Процесс использования
- Установка ключа API::
import os os.environ["LLM_API_KEY"] = "YOUR_OPENAI_API_KEY"Или:
import cognee cognee.config.set_llm_api_key("YOUR_OPENAI_API_KEY") - Создание файлов .env: Создайте файл .env и задайте ключ API:
LLM_API_KEY=YOUR_OPENAI_API_KEY - Использование различных провайдеров LLM: О настройке различных провайдеров LLM см. в документации.
- Результаты визуализации: Если используется сеть, создайте учетную запись Graphistry и настройте ее:
cognee.config.set_graphistry_config({ "username": "YOUR_USERNAME", "password": "YOUR_PASSWORD" })
Основные функции
- извлечение данных: Извлечение данных с помощью конвейера ECL от Cognee, который поддерживает множество источников и форматов данных.
- Осведомленность о данных: Обработка и анализ данных с помощью когнитивного модуля Cognee для уменьшения галлюцинаций.
- Загрузка данныхЗагрузка обработанных данных в целевую базу данных или хранилище. Поддерживается широкий спектр баз данных и векторных хранилищ.
Основные функции Процедура работы
- Взаимосвязь и поиск исторических данных: Легкая взаимосвязь и поиск прошлых разговоров, документов и аудиозаписей с помощью модульной конструкции Cognee.
- Снижение нагрузки на разработчиков: Предоставьте подробную документацию и примеры, чтобы снизить порог для разработчиков и сократить время и стоимость разработки.
Посетите официальный сайт, чтобы узнать больше о рамах cognee.
Читайте обзор освоения теоретических основ когнитивной деятельности
Просмотрите учебники и учебные материалы, чтобы начать работу
Команда основной подсказки
classify_content: классифицированный контент
You are a classification engine and should classify content. Make sure to use one of the existing classification options nad not invent your own.
The possible classifications are:
{
"Natural Language Text": {
"type": "TEXT",
"subclass": [
"Articles, essays, and reports",
"Books and manuscripts",
"News stories and blog posts",
"Research papers and academic publications",
"Social media posts and comments",
"Website content and product descriptions",
"Personal narratives and stories"
]
},
"Structured Documents": {
"type": "TEXT",
"subclass": [
"Spreadsheets and tables",
"Forms and surveys",
"Databases and CSV files"
]
},
"Code and Scripts": {
"type": "TEXT",
"subclass": [
"Source code in various programming languages",
"Shell commands and scripts",
"Markup languages (HTML, XML)",
"Stylesheets (CSS) and configuration files (YAML, JSON, INI)"
]
},
"Conversational Data": {
"type": "TEXT",
"subclass": [
"Chat transcripts and messaging history",
"Customer service logs and interactions",
"Conversational AI training data"
]
},
"Educational Content": {
"type": "TEXT",
"subclass": [
"Textbook content and lecture notes",
"Exam questions and academic exercises",
"E-learning course materials"
]
},
"Creative Writing": {
"type": "TEXT",
"subclass": [
"Poetry and prose",
"Scripts for plays, movies, and television",
"Song lyrics"
]
},
"Technical Documentation": {
"type": "TEXT",
"subclass": [
"Manuals and user guides",
"Technical specifications and API documentation",
"Helpdesk articles and FAQs"
]
},
"Legal and Regulatory Documents": {
"type": "TEXT",
"subclass": [
"Contracts and agreements",
"Laws, regulations, and legal case documents",
"Policy documents and compliance materials"
]
},
"Medical and Scientific Texts": {
"type": "TEXT",
"subclass": [
"Clinical trial reports",
"Patient records and case notes",
"Scientific journal articles"
]
},
"Financial and Business Documents": {
"type": "TEXT",
"subclass": [
"Financial reports and statements",
"Business plans and proposals",
"Market research and analysis reports"
]
},
"Advertising and Marketing Materials": {
"type": "TEXT",
"subclass": [
"Ad copies and marketing slogans",
"Product catalogs and brochures",
"Press releases and promotional content"
]
},
"Emails and Correspondence": {
"type": "TEXT",
"subclass": [
"Professional and formal correspondence",
"Personal emails and letters"
]
},
"Metadata and Annotations": {
"type": "TEXT",
"subclass": [
"Image and video captions",
"Annotations and metadata for various media"
]
},
"Language Learning Materials": {
"type": "TEXT",
"subclass": [
"Vocabulary lists and grammar rules",
"Language exercises and quizzes"
]
},
"Audio Content": {
"type": "AUDIO",
"subclass": [
"Music tracks and albums",
"Podcasts and radio broadcasts",
"Audiobooks and audio guides",
"Recorded interviews and speeches",
"Sound effects and ambient sounds"
]
},
"Image Content": {
"type": "IMAGE",
"subclass": [
"Photographs and digital images",
"Illustrations, diagrams, and charts",
"Infographics and visual data representations",
"Artwork and paintings",
"Screenshots and graphical user interfaces"
]
},
"Video Content": {
"type": "VIDEO",
"subclass": [
"Movies and short films",
"Documentaries and educational videos",
"Video tutorials and how-to guides",
"Animated features and cartoons",
"Live event recordings and sports broadcasts"
]
},
"Multimedia Content": {
"type": "MULTIMEDIA",
"subclass": [
"Interactive web content and games",
"Virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) experiences",
"Mixed media presentations and slide decks",
"E-learning modules with integrated multimedia",
"Digital exhibitions and virtual tours"
]
},
"3D Models and CAD Content": {
"type": "3D_MODEL",
"subclass": [
"Architectural renderings and building plans",
"Product design models and prototypes",
"3D animations and character models",
"Scientific simulations and visualizations",
"Virtual objects for AR/VR environments"
]
},
"Procedural Content": {
"type": "PROCEDURAL",
"subclass": [
"Tutorials and step-by-step guides",
"Workflow and process descriptions",
"Simulation and training exercises",
"Recipes and crafting instructions"
]
}
}
generate_cog_layers: генерировать когнитивные слои
You are tasked with analyzing `{{ data_type }}` files, especially in a multilayer network context for tasks such as analysis, categorization, and feature extraction. Various layers can be incorporated to capture the depth and breadth of information contained within the {{ data_type }}.
These layers can help in understanding the content, context, and characteristics of the `{{ data_type }}`.
Your objective is to extract meaningful layers of information that will contribute to constructing a detailed multilayer network or knowledge graph.
Approach this task by considering the unique characteristics and inherent properties of the data at hand.
VERY IMPORTANT: The context you are working in is `{{ category_name }}` and the specific domain you are extracting data on is `{{ category_name }}`.
Guidelines for Layer Extraction:
Take into account: The content type, in this case, is: `{{ category_name }}`, should play a major role in how you decompose into layers.
Based on your analysis, define and describe the layers you've identified, explaining their relevance and contribution to understanding the dataset. Your independent identification of layers will enable a nuanced and multifaceted representation of the data, enhancing applications in knowledge discovery, content analysis, and information retrieval.
generate_graph_prompt: генерировать подсказки для графиков
You are a top-tier algorithm
designed for extracting information in structured formats to build a knowledge graph.
- **Nodes** represent entities and concepts. They're akin to Wikipedia nodes.
- **Edges** represent relationships between concepts. They're akin to Wikipedia links.
- The aim is to achieve simplicity and clarity in the
knowledge graph, making it accessible for a vast audience.
YOU ARE ONLY EXTRACTING DATA FOR COGNITIVE LAYER `{{ layer }}`
## 1. Labeling Nodes
- **Consistency**: Ensure you use basic or elementary types for node labels.
- For example, when you identify an entity representing a person,
always label it as **"Person"**.
Avoid using more specific terms like "mathematician" or "scientist".
- Include event, entity, time, or action nodes to the category.
- Classify the memory type as episodic or semantic.
- **Node IDs**: Never utilize integers as node IDs.
Node IDs should be names or human-readable identifiers found in the text.
## 2. Handling Numerical Data and Dates
- Numerical data, like age or other related information,
should be incorporated as attributes or properties of the respective nodes.
- **No Separate Nodes for Dates/Numbers**:
Do not create separate nodes for dates or numerical values.
Always attach them as attributes or properties of nodes.
- **Property Format**: Properties must be in a key-value format.
- **Quotation Marks**: Never use escaped single or double quotes within property values.
- **Naming Convention**: Use snake_case for relationship names, e.g., `acted_in`.
## 3. Coreference Resolution
- **Maintain Entity Consistency**:
When extracting entities, it's vital to ensure consistency.
If an entity, such as "John Doe", is mentioned multiple times
in the text but is referred to by different names or pronouns (e.g., "Joe", "he"),
always use the most complete identifier for that entity throughout the knowledge graph.
In this example, use "John Doe" as the entity ID.
Remember, the knowledge graph should be coherent and easily understandable,
so maintaining consistency in entity references is crucial.
## 4. Strict Compliance
Adhere to the rules strictly. Non-compliance will result in termination"""
read_query_prompt: чтение запроса
from os import path
import logging
from cognee.root_dir import get_absolute_path
def read_query_prompt(prompt_file_name: str):
"""Read a query prompt from a file."""
try:
file_path = path.join(get_absolute_path("./infrastructure/llm/prompts"), prompt_file_name)
with open(file_path, "r", encoding = "utf-8") as file:
return file.read()
except FileNotFoundError:
logging.error(f"Error: Prompt file not found. Attempted to read: %s {file_path}")
return None
except Exception as e:
logging.error(f"An error occurred: %s {e}")
return None
render_prompt: подсказка для рендеринга
from jinja2 import Environment, FileSystemLoader, select_autoescape
from cognee.root_dir import get_absolute_path
def render_prompt(filename: str, context: dict) -> str:
"""Render a Jinja2 template asynchronously.
:param filename: The name of the template file to render.
:param context: The context to render the template with.
:return: The rendered template as a string."""
# Set the base directory relative to the cognee root directory
base_directory = get_absolute_path("./infrastructure/llm/prompts")
# Initialize the Jinja2 environment to load templates from the filesystem
env = Environment(
loader = FileSystemLoader(base_directory),
autoescape = select_autoescape(["html", "xml", "txt"])
)
# Load the template by name
template = env.get_template(filename)
# Render the template with the provided context
rendered_template = template.render(context)
return rendered_template
summarize_content: краткое содержание
You are a summarization engine and you should sumamarize content. Be brief and concise
© заявление об авторских правах
Авторское право на статью Круг обмена ИИ Пожалуйста, не воспроизводите без разрешения.
Похожие статьи

Нет комментариев...