VITA: Open Source Multimodal Large Language Model for Real-Time Interaction between Vision and Speech
General Introduction
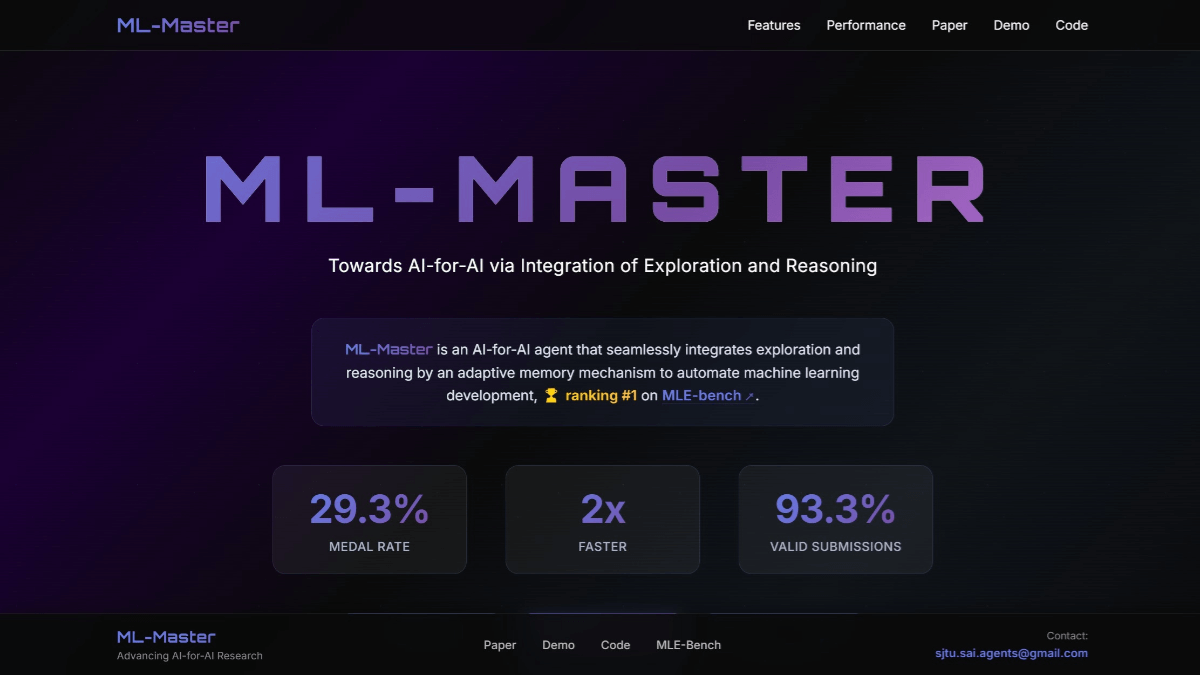
VITA is a leading open source interactive multimodal large language modeling project, pioneering the ability to achieve true full multimodal interaction. The project launched VITA-1.0 in August 2024, pioneering the first open-source interactive multimodal large language model, and in December 2024, the project launched a major upgrade version, VITA-1.5, which significantly improves both the interaction experience and performance.The VITA model supports multi-modal inputs and outputs, such as image, video, and audio, and is equipped with real-time interaction capabilities, significantly reducing the end-to-end voice interaction latency from 4 seconds to 1.5 seconds. The VITA model supports multi-modal inputs and outputs such as image, video, and audio, and has real-time interaction capability, which significantly reduces the end-to-end voice interaction latency from 4 seconds to 1.5 seconds, greatly improving the user experience. As a fully open source project, VITA provides an ideal platform for researchers and developers to explore multimodal AI.

Function List
- Multi-modal Input Processing: Supports image, video, audio and other forms of inputs
- Real-time voice interaction: end-to-end voice interaction latency of only 1.5 seconds
- Visual analytics capabilities: powerful image and video comprehension and analysis capabilities
- Audio processing: supports speech recognition and speech synthesis
- Cross-modal understanding: towards intelligent correlation between text, images, and audio
- Open source support: complete training and inference code is open
- Pre-trained models: multiple versions of pre-trained models are available
- Flexible deployment options: supports multiple hardware platform deployments
VITA-1.5 Overview
On August 12, 2024, we released the VITA-1.0This is The first open-source interactive all-in-one multimodal macrolanguage model. And now (December 20, 2024), we bring you the New version VITA-1.5!
What's new in VITA-1.5?
We are pleased to present VITA-1.5, which introduced a series of advances:
- Significantly reduce interaction latency.. End-to-end voice interaction latency has increased from Approx. 4 seconds Reduction to 1.5 seconds, which enables almost instantaneous interaction and greatly enhances the user experience.
- Enhanced multimodal performanceThe In MME,MMBench cap (a poem) MathVista The average performance in multimodal benchmarks such as this is significantly improved from 59.8 raise it to 70.8The
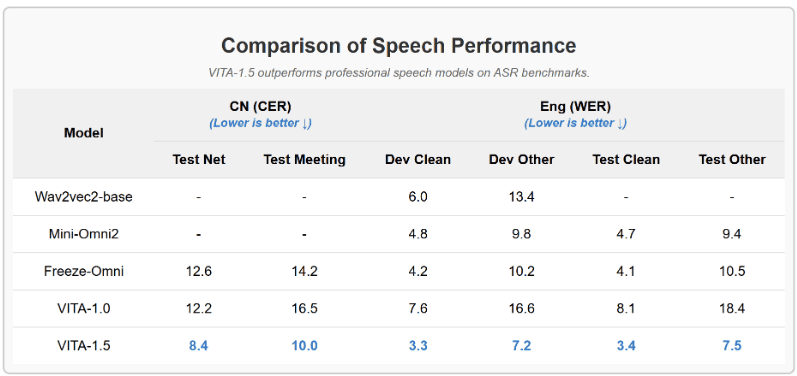
- Speech Processing Capability Enhancement.. A new level of speech processing power was achieved, with ASR WER (Word Error Rate, Test Other) increasing from 18.4 Reduce to 7.5. In addition, we used End-to-End TTS Module Replaces the stand-alone TTS module of VITA-1.0, which accepts as input the embedding of large language models.
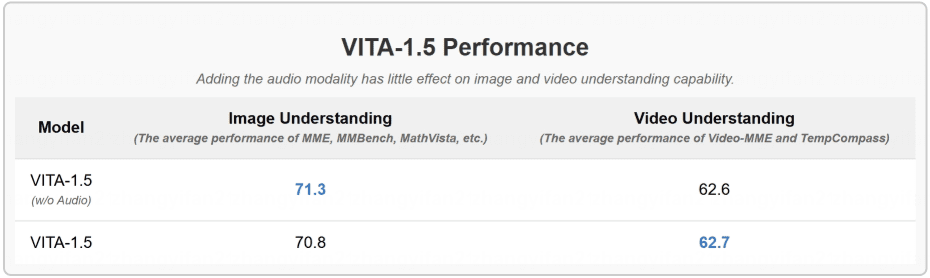
- Progressive training strategies. In this way, the inclusion of the speech module has little effect on the other multimodal performance (visual-verbal). The average performance of image understanding only decreased from 71.3 to 70.8.
Results
- Evaluation of Image and Video Understanding Benchmark Tests
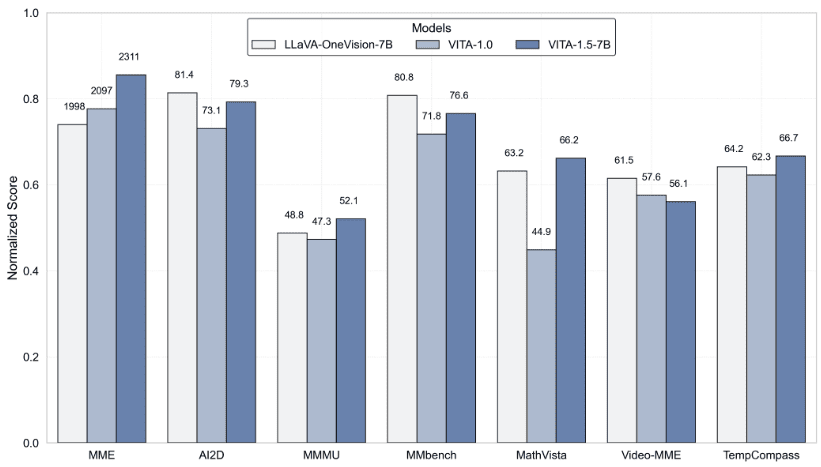
- VITA-1.5 Outperforms Professional Speech Models in ASR Benchmarks
- The inclusion of audio modality has little to no effect on image and video comprehension
Using Help
1. Environment configuration and installation
1.1 Foundation requirements:
- Python environment
- PyTorch framework
- CUDA support (GPU acceleration recommended)
1.2 Installation steps:
# 克隆项目仓库
git clone https://github.com/VITA-MLLM/VITA.git
cd VITA
# 安装依赖
pip install -r requirements.txt
2. Use of models
2.1 Loading the pre-trained model:
from vita.model.builder import load_pretrained_model
from vita.conversation import conv_templates
from vita.util.mm_utils import get_model_name_from_path
# 加载模型
model_path = 'VITA/vita'
model_name = get_model_name_from_path(model_path)
tokenizer, model, image_processor, _ = load_pretrained_model(
model_path,
None,
model_name,
model_type='mixtral-8x7b',
device_map='auto'
)
2.2 Audio processing configuration:
# 初始化音频编码器
audio_encoder = model.get_audio_encoder()
audio_encoder.to(dtype=torch.float16)
audio_processor = audio_encoder.audio_processor
3. Real-time interactive functions
- Supports real-time voice input and response
- Integrated Image Recognition and Analysis
- Supports multi-round dialog interactions
- Provide a complete dialog template system
4. Use of advanced functions
4.1 Multimodal Input Processing:
- Supports batch image processing
- Real-time video streaming analysis
- Audio stream processing and synthesis
4.2 Model training and fine-tuning:
- Provides complete training scripts
- Support for continuous learning features
- Customized dataset training support
5. Evaluation and testing
- Supports mainstream multimodal evaluation benchmarks
- Integrated VLMEvalKit evaluation tool
- Provide detailed performance test metrics
6. Cautions
- GPUs are recommended for model inference
- Pay attention to memory management, especially when dealing with large multimodal inputs
- Regularly check for project updates for the latest features and optimizations
© Copyright notes
Article copyright AI Sharing Circle All, please do not reproduce without permission.
Related posts

No comments...