HtmlRAG: Building an Efficient HTML Retrieval Enhanced Generation System, Optimizing HTML Document Retrieval and Processing in RAG Systems
General Introduction
HtmlRAG is an innovative open source project focused on improving retrieval enhancement generation (RAG) approach to HTML document processing in the system. The project presents a novel approach that argues that using HTML formatting in RAG systems is more efficient than plain text. The project encompasses a complete data processing flow, from query rewriting to HTML document crawling to an evaluation system for answer generation. It supports the processing of several mainstream datasets, including ASQA, HotpotQA, NQ, etc., and provides detailed evaluation metrics to measure the system performance. The project not only provides a source code implementation, but also includes preprocessed datasets and evaluation tools, enabling researchers to easily reproduce the results and make further improvements.
Paper address: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2411.02959
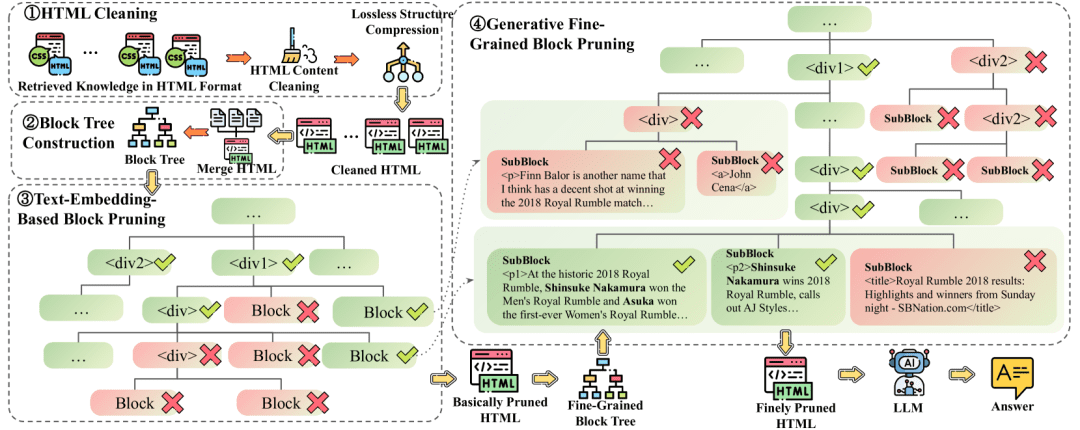
Proposes HtmlRAG , which uses HTML rather than plain text as the format for external knowledge in the RAG system. To cope with the long context brought by HTML, lossless HTML cleanup and Two-Step Block-Tree-Based HTML pruning are proposed.
Non-destructive HTML cleanup: This cleanup process removes only completely irrelevant content and compresses redundant structures, preserving all semantic information in the original HTML. Lossless HTML cleanup compressed HTML is suitable for RAG systems with long context LLMs and an unwillingness to lose any information before generation. HTML pruning based on two-step block trees: Block tree-based HTML pruning consists of two steps, both of which are performed on the block tree structure.The first pruning step uses the embedding model to compute scores for blocksbut (not)The second step uses the path to generate the model. The first step deals with the results of the non-destructive HTML cleanup, while the second step deals with the results of the first pruning step.
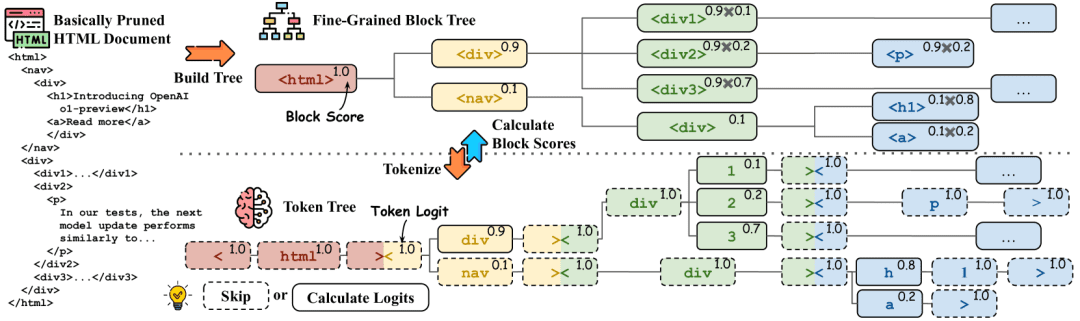
Block score calculation. The block tree is converted to a token tree by a splitter, and the corresponding HTML tags and tokens are marked with the same color. Token generation probabilities are shown in the upper right corner, and tokens in the dashed box do not require inference. In the upper right corner of the block tree, the block probabilities are shown, and the probabilities can be derived from the corresponding token probabilities
Example command:
**HTML**: “{HTML}”
**问题**: **{Question}**
您的任务是从 HTML 文档中识别与给定问题最相关的文本片段。该文本片段可以是对事实的直接释义,或可用作推断该事实的支持性证据。
文本片段的整体长度应超过 20 个单词且少于 300 个单词。您需要提供该文本片段在 HTML 文档中的路径。
输出示例为:
<html1><body><div2><p>一些关键信息...
输出:
<html1><body><div2><p>在历史性的 2018 年皇家大战中,Shinsuke Nakamura 赢得了男子皇家大战. . .

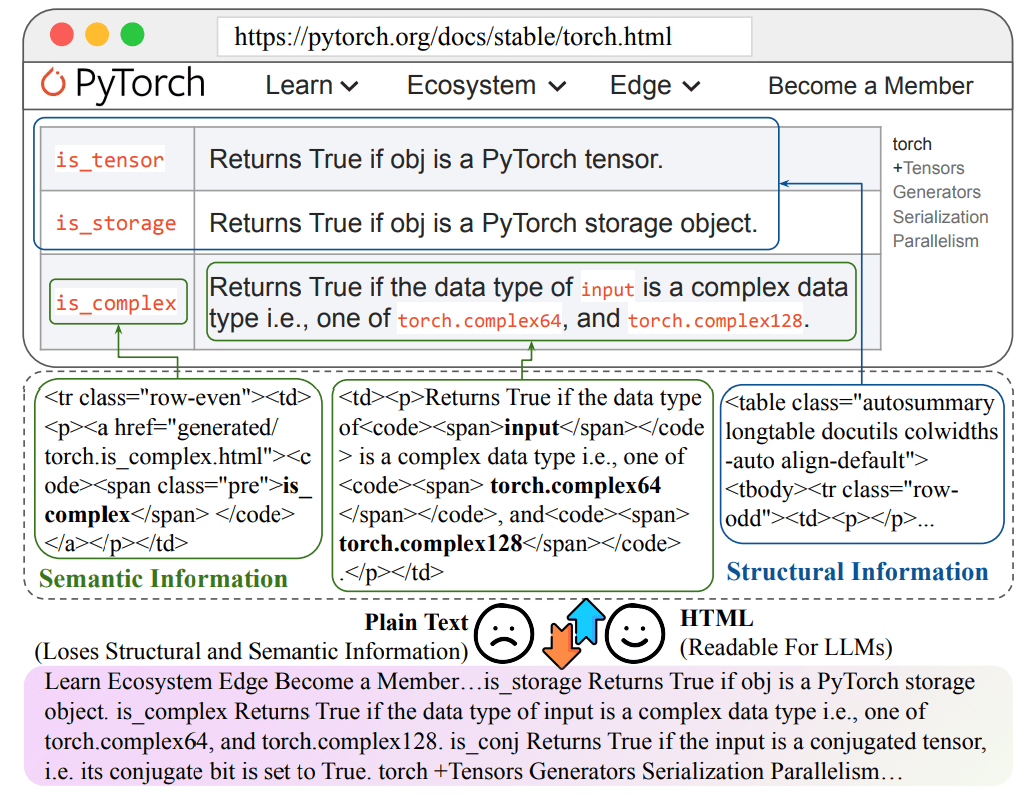
Loss of information when converting HTML to plain text
Function List
- Query processing and rewriting capabilities to support decomposition of complex problems into subqueries
- HTML document crawling and processing system, preserving document structure information
- Multi-dataset support (ASQA, HotpotQA, NQ, TriviaQA, MuSiQue, ELI5)
- Complete assessment framework, including multiple dimensions such as correctness and relevance of answers
- Custom dataset processing support, allowing users to work with their own data
- Integrated Bing search function for retrieving relevant web pages
- Provide a detailed scoring system with a variety of assessment metrics including ROUGE scores
- Support for integration with the LangChain framework
- Results visualization and analysis tools
Using Help
1. Environmental configuration
First you need to clone the project repository and install the necessary dependencies:
git clone https://github.com/plageon/HtmlRAG
cd HtmlRAG
pip install -r requirements.txt
2. Data set preparation
The project supports two ways of using data:
- Use a pre-processed dataset:
- The dataset is stored in the html_data folder
- The full test dataset can be downloaded from huggingface: HtmlRAG-test
- Supported dataset formats include ASQA, HotpotQA, NQ, etc.
- Use custom data:
- Prepare the query file in .jsonl format, with each line containing the following fields:
{ "id": "unique_id", "question": "query_text", "answers": ["answer_text_1", "answer_text_2"] }
- Prepare the query file in .jsonl format, with each line containing the following fields:
3. Flow of use of major functions
query processing
- Query Rewrite:
- The system automatically breaks down complex questions into multiple subqueries
- The rewrite result is stored in the rewrite_method_result field of the json object
HTML document processing
- Page Crawl:
- The system uses Bing to search for relevant URLs
- Automatic crawling of static HTML documents
- Retain information about the HTML structure of the document
Evaluation systems
- Evaluate indicator configurations:
- Assessment of correctness of answers
- Assessment of answer relevance
- ROUGE score calculation
- Customized assessment indicator settings
- Use of assessment tools:
from ragas.metrics import AnswerRelevancy
from langchain.embeddings import HuggingFaceEmbeddings
# 初始化评估器
embeddings = HuggingFaceEmbeddings('BAAI/bge-base-en')
answer_relevancy = AnswerRelevancy(embeddings=embeddings)
# 加载模型
answer_relevancy.init_model()
# 运行评估
results = answer_relevancy.score(dataset)
4. Analysis and optimization of results
- Analysis of assessment results using the visualization tools provided
- Adjustment of system parameters based on assessment indicators
- Optimizing Query Rewriting Strategies and Document Processing Methods
5. Cautions
- Ensure enough storage space to handle HTML data
- Compliance with API usage limits and rate limits
- Regularly update dependency packages for the latest features
- Pay attention to the correctness of the data format
- GPUs are recommended to accelerate large-scale data processing
Reference note on HTML document cleaning
HTML cleaning rules (Clean Patterns)
def clean_html(html: str) -> str: # 1. 使用BeautifulSoup解析HTML soup = bs4.BeautifulSoup(html, 'html.parser') # 2. 调用simplify_html进行简化处理 html = simplify_html(soup) # 3. 调用clean_xml清理XML标记 html = clean_xml(html) return html

1. HTML document processing related words (the following content is not project code)
# HTML清洗提示词
CLEAN_HTML_PROMPT = """
任务:清洗HTML文档,保留有效信息
输入:原始HTML文档
要求:
1. 移除:
- JavaScript代码 (<script>标签)
- CSS样式信息 (<style>标签)
- HTML注释
- 空白标签
- 多余属性
2. 保留:
- 主要内容标签(<title>, <p>, <div>, <h1>-<h6>等)
- 文本内容
- 结构关系
输出:清洗后的HTML文本
"""
# HTML分块提示词
HTML_BLOCK_PROMPT = """
任务:将HTML文档分割成语义完整的块
输入:
- 清洗后的HTML文档
- 最大块大小:{max_words}词
要求:
1. 保持HTML标签的层级结构
2. 确保每个块的语义完整性
3. 记录块的层级路径
4. 控制每个块的大小不超过限制
输出:JSON格式的块列表,包含:
{
"blocks": [
{
"content": "块内容",
"path": "HTML路径",
"depth": "层级深度"
}
]
}
"""
2. Cue words related to block tree construction
# 块树节点评分提示词
BLOCK_SCORING_PROMPT = """
任务:评估HTML块与问题的相关性
输入:
- 问题:{question}
- HTML块:{block_content}
- 块路径:{block_path}
要求:
1. 计算语义相关性分数(0-1)
2. 考虑以下因素:
- 文本相似度
- 结构重要性
- 上下文关联
输出:
{
"score": float, # 相关性分数
"reason": "评分理由"
}
"""
# 块树剪枝提示词
TREE_PRUNING_PROMPT = """
任务:决定是否保留HTML块
输入:
- 问题:{question}
- 当前块:{current_block}
- 父级块:{parent_block}
- 子块列表:{child_blocks}
要求:
1. 分析块的重要性:
- 与问题的相关性
- 在文档结构中的作用
- 与父子块的关系
2. 生成保留/删除决策
输出:
{
"action": "keep/remove",
"confidence": float, # 决策置信度
"reason": "决策理由"
}
"""
3. Knowledge retrieval-related terms
# 相关性计算提示词
RELEVANCE_PROMPT = """
任务:计算文档片段与问题的相关性
输入:
- 问题:{question}
- 文档片段:{text_chunk}
评估标准:
1. 直接相关性:内容直接回答问题的程度
2. 间接相关性:提供背景或补充信息的程度
3. 信息完整性:回答是否完整
输出:
{
"relevance_score": float, # 相关性分数0-1
"reason": "评分理由",
"key_matches": ["关键匹配点1", "关键匹配点2", ...]
}
"""
# 答案生成提示词
ANSWER_GENERATION_PROMPT = """
任务:根据相关文档生成答案
输入:
- 用户问题:{question}
- 相关文档:{relevant_docs}
- 文档评分:{doc_scores}
要求:
1. 综合高相关性文档信息
2. 保持答案的准确性
3. 确保回答完整且连贯
4. 必要时标注信息来源
输出格式:
{
"answer": "生成的答案",
"sources": ["使用的文档来源"],
"confidence": float # 答案置信度
}
"""
4. Assessment of relevant prompts
# 答案评估提示词
EVALUATION_PROMPT = """
任务:评估生成答案的质量
输入:
- 原始问题:{question}
- 生成答案:{generated_answer}
- 参考答案:{reference_answer}
评估维度:
1. 正确性:信息是否准确
2. 完整性:是否完整回答问题
3. 相关性:内容与问题的相关程度
4. 连贯性:表述是否清晰连贯
输出:
{
"scores": {
"correctness": float,
"completeness": float,
"relevance": float,
"coherence": float
},
"feedback": "详细评估意见"
}
"""
# 错误分析提示词
ERROR_ANALYSIS_PROMPT = """
任务:分析答案中的潜在错误
输入:
- 生成答案:{answer}
- 参考资料:{reference_docs}
分析要点:
1. 事实准确性检查
2. 逻辑推理验证
3. 信息来源核实
输出:
{
"errors": [
{
"type": "错误类型",
"description": "错误描述",
"correction": "建议修正"
}
],
"reliability_score": float # 可信度评分
}
"""© Copyright notes
Article copyright AI Sharing Circle All, please do not reproduce without permission.
Related articles

No comments...