RoboOS 2.0 - Wisdom Spectrum's Open Source Cross-Ontology Embodied Brain-Size Collaboration Framework
What is RoboOS 2.0
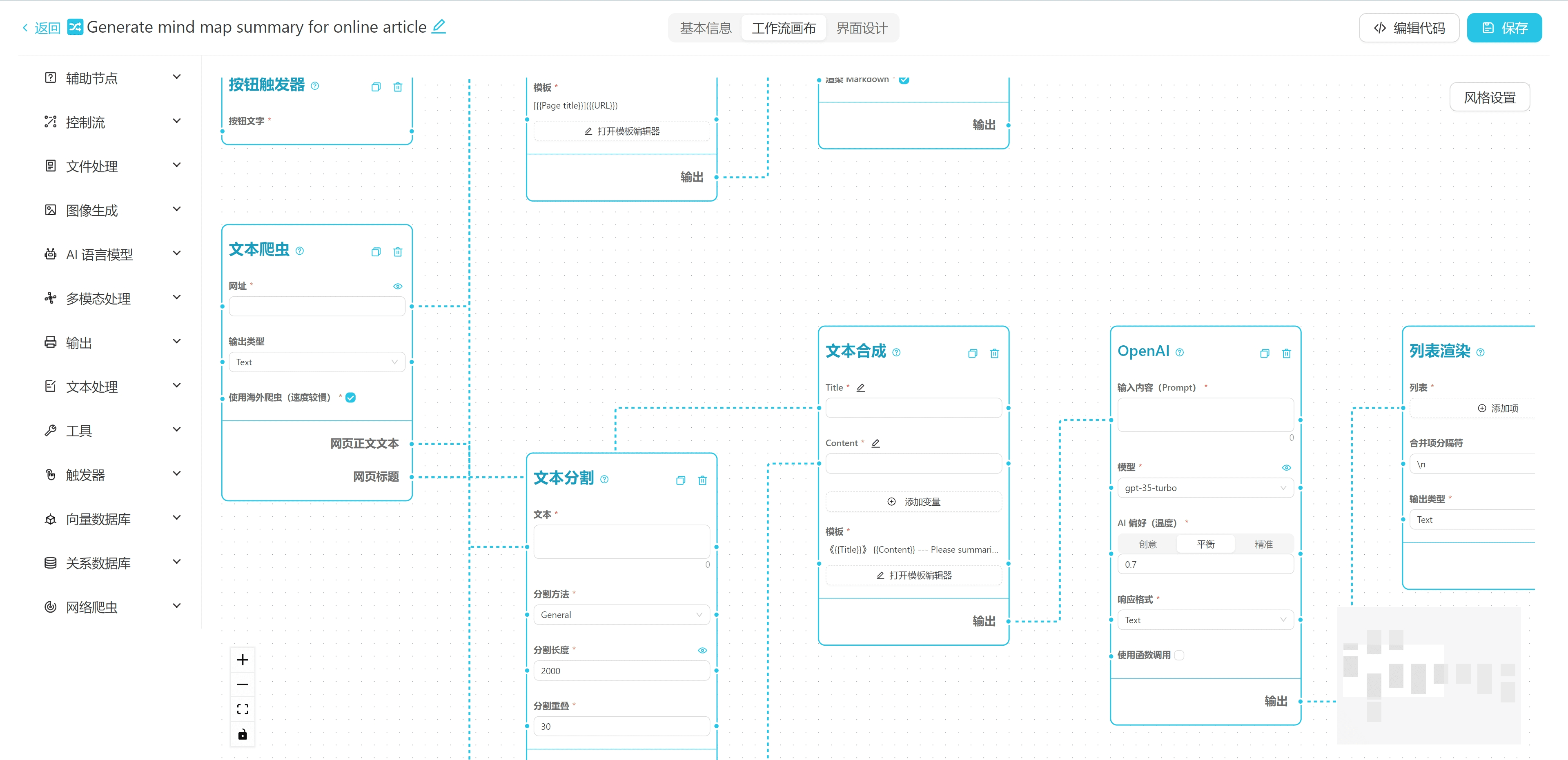
RoboOS 2.0 is an open-source framework for cross ontology brain collaboration, promoting the transformation of robots from single intelligence to collaborative group intelligence. RoboOS 2.0 uses a "big brain" architecture to realize efficient division of labor, with the cloud brain responsible for complex decision-making and collaboration, and the small brain module focusing on the execution of specific skills. The framework supports multi-robot collaboration with lightweight deployment, standardized interfaces, and real-time sensing capabilities, which can be quickly adapted to different hardware and task requirements. The optimized end-cloud collaboration mechanism and multimodal data processing capability of the framework further enhance the adaptability and execution efficiency of robots in dynamic environments, which is widely applicable to logistics, family services, industrial production and other scenarios.

RoboOS 2.0 Key Features
- Multiple robots working together: The ability to flexibly assign tasks and allow multiple robots to perform efficiently at the same time is particularly suitable for complex scenarios and dramatically improves efficiency.
- A clear division of labor between large and small brain structures: The cloud brain focuses on complex decision-making and collaborative scheduling, while the cerebellar module is responsible for the precise execution of specific skills, and the two work well together.
- Lightweight Deployment Advantage: With the help of advanced MCP protocols and serverless architecture, dramatically reducing the difficulty of development, enabling rapid deployment and simplifying the development process.
- Standardized interface design: Supports one-click adaptation of robotics skill modules developed by global developers.
- Real-time sensing and modeling capabilities: A new multi-ontology spatio-temporal memory scene graph sharing mechanism has been added for real-time sensing and modeling in dynamic environments to enhance adaptability to complex environments.
- Task monitoring and closed-loop feedback: Introducing a multi-granularity task monitoring module to track the progress of tasks in real time and ensure that tasks are completed stably and reliably.
RoboOS 2.0 official website address
- Project website:: https://github.com/FlagOpen/RoboOS
- GitHub repository:: https://github.com/FlagOpen/RoboOS
- arXiv Technical Paper:: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2505.03673
How to use RoboOS 2.0
- Visit the official website: Visit the RoboOS 2.0 official website or GitHub repository.
- environmental preparation::
- hardware requirement: Ensure that supported robotic hardware devices are available and that interfaces and compatibility are understood.
- software environment: Install the necessary dependent libraries and development tools, such as Python, ROS (if applicable), etc.
- Installation and Configuration::
- clone warehouse: Clone the RoboOS 2.0 GitHub repository locally:
git clone https://github.com/FlagOpen/RoboOS.git
cd RoboOS- Installation of dependencies: Install the necessary dependencies according to the project documentation, which can usually be done with the following commands:
pip install -r requirements.txt- configuration file: Depending on the hardware and application scenario, modify the configuration file (e.g.
config.yaml), set robot parameters, network address, etc.
- Deployment of the brain module::
- Cloud Deployment: If you need to use the Cloud Brain module, deploy it to a supported cloud platform (e.g. AWS, Azure, or AliCloud). Follow the instructions in the documentation to set it up.
- local test: Run the brain module on a local machine for development and testing.
- Deployment of cerebellar modules::
- hardware adaptation: Deploy the cerebellum module to the robot based on the robot hardware. Ensure that the cerebellum module can communicate with the brain module.
- Skills Registration: Register and manage robot skill modules using the RoboOS 2.0 Skill Store feature.
- Operation and Commissioning
- activation system: Follow the instructions in the documentation to activate the cerebral and cerebellar modules.
# 启动大脑模块
python brain_module.py
# 启动小脑模块
python cerebellum_module.py- real time monitoring: Use the task monitoring module to view task execution in real time to ensure that the system operates normally.
- Debugging Optimization: Adjust parameters to optimize performance based on operating conditions.
RoboOS 2.0 Core Benefits
- Efficient synergies: Through the big and small brain architecture, it realizes the efficient division of labor between high-level cognition and specialized skill execution, supports multi-robot collaboration, dynamically assigns tasks and executes them in parallel, and greatly improves the efficiency of task execution.
- Lightweight and easy to deploy: Integrate MCP protocol and serverless architecture to lower the development threshold and simplify the deployment process, so that the robotics system can be quickly online, reducing development time and cost.
- Powerful environmental awarenessIt is equipped with real-time shared memory mechanism and multi ontology spatio-temporal memory scene graph sharing mechanism, dynamically updating the environment state, supporting real-time perception and modeling under dynamic environment, and enhancing the robot's adaptability to the complex environment.
- Standardization and compatibilityIt provides standardized interfaces to eliminate adaptation differences between different hardware and manufacturers, and supports one-click adaptation of robot skill modules created by global developers, greatly expanding the application scenarios and flexibility of the system.
- System-level optimization: System-level optimization of the end-to-end inference link, significant improvement in overall performance, significant improvement in end-cloud communication efficiency, and extremely low average response latency across the link to ensure efficient collaboration between multiple intelligences.
- Task Monitoring and Reliability: Introducing a multi-granularity task monitoring module, realizing closed-loop feedback of tasks, improving the stability and success rate of task execution, ensuring reliable completion of tasks, and enhancing the reliability and practicability of the system.
Who is RoboOS 2.0 for?
- Robot developers: Provide standardized interfaces and lightweight deployment to reduce the development threshold, both individual developers and team developers can quickly get started and efficiently develop complex robotics applications.
- (scientific) researcher: To provide an ideal experimental platform for researchers engaged in robotics, artificial intelligence and multi-intelligent body system research, and to assist academic research and teaching and experimentation in university laboratories.
- Business and Industrial UsersThe multi-robot collaboration and powerful tasking capabilities make it the ideal choice for companies in industries such as logistics, warehousing, manufacturing and healthcare, where productivity and automation levels can be significantly improved.
- Households and Services: To help home service robots better adapt to dynamic home environments and accomplish tasks such as housework, applicable to the development of robotic applications in hotels, restaurants and other service industries to improve service efficiency and quality.
- educational organization: To serve as a tool for primary and secondary education, to stimulate students' interest in robotics and AI, and to provide a practical platform for vocational training, helping students and practitioners to acquire relevant skills.
© Copyright notes
Article copyright AI Sharing Circle All, please do not reproduce without permission.
Related posts

No comments...