CoT (Chain-of-Thought) Chain of Thought
AKA: Chain of Thought
Definition and rationale for Chain-of-Thought
"Chain-of-Thought" (CoT for short) is a method of thinking based on the principle of creating a chain of thinking consisting of a series of linked thinking steps. The method helps people think more systematically about problems and generate creative ideas by breaking down the thinking process into a series of organized steps. The method is applicable to a variety of thinking scenarios, such as innovation, decision-making, problem solving, etc. The core idea of the CoT method is to break down a large problem into a number of smaller problems, and then to break down each small problem into even smaller problems until each problem can be answered in a simple, unambiguous way. In this way, one can understand the problem more clearly and find a better solution.
We can compare Chain-of-Thought to a jigsaw puzzle, where each piece represents an aspect of a problem, and only by connecting these pieces can we get a complete answer. For example, when we are learning a new knowledge, we can use Chain-of-Thought to establish the relationship between various knowledge points, so as to better understand and memorize the knowledge; when we are solving a problem, we can use Chain-of-Thought to break down the problem into multiple sub-problems, and then solve them step by step to finally get a complete solution.
Interpretation of the big data field
The Chain of Thought (CoT) prompting process is a recently developed prompting method that encourages large language models to explain their reasoning processes. The figure below shows a comparison of the few shot standard prompt (left) with the Chain of Thought prompting process (right).
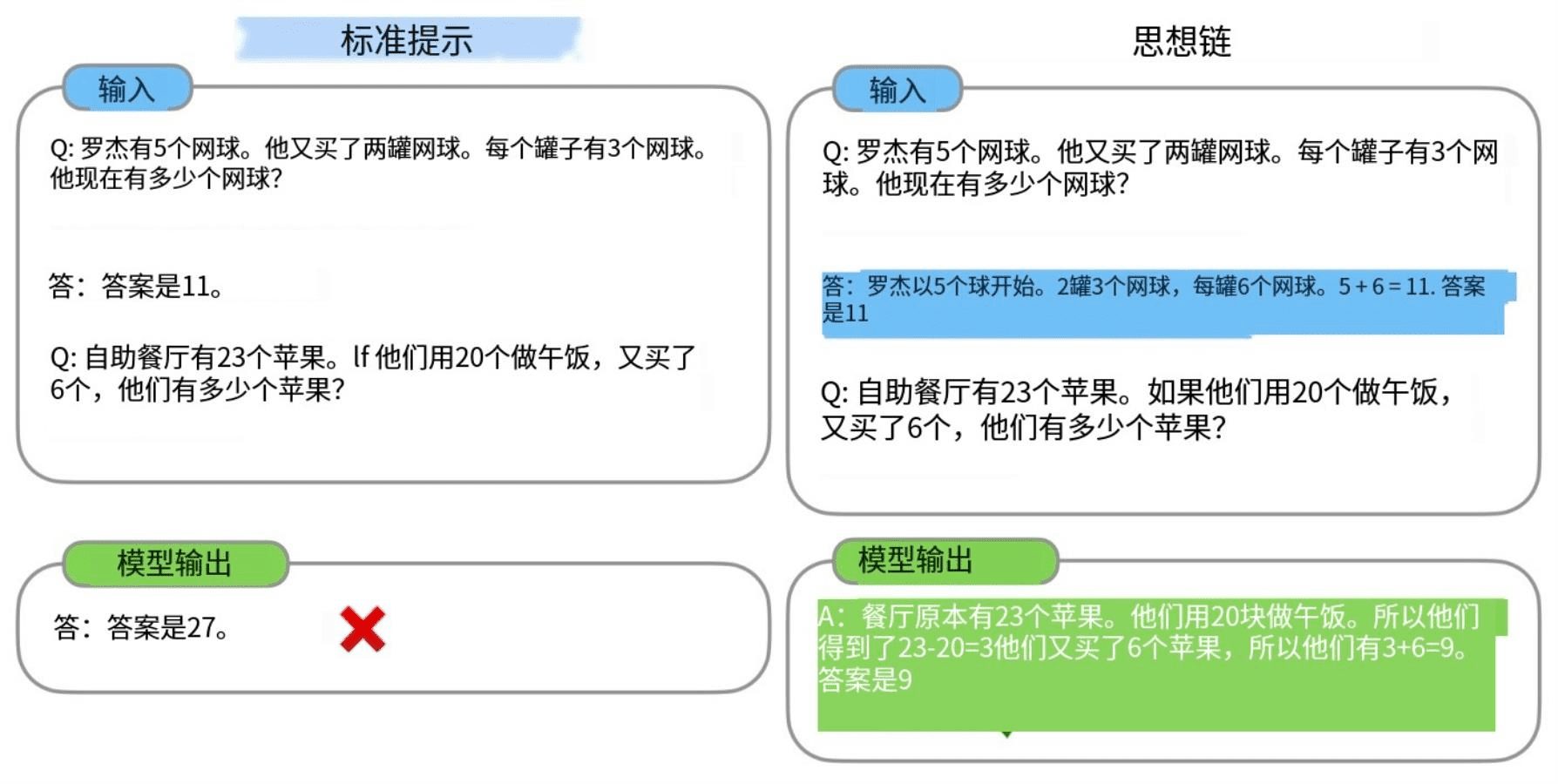
Come up with a new question on how to get the big model to compute this question absolutely correctly:
A chicken lays six eggs a day, I collected the eggs once today and ate half of them. The next day I collected the eggs again and ate two of them, and on the third day I collected the eggs again, how many eggs do I have left now?
existWei et al. (2022) (opens in a new tabThe Chained Thinking (CoT) prompts introduced in achieve complex reasoning power through intermediate reasoning steps. You can combine this with sample less prompts to get better results for more complex tasks where reasoning precedes answering.
The main idea of thought chaining is to explain the reasoning process in samples by showing some small number of exemplars to the big language model, which also displays the reasoning process when answering the prompts. This explanation of reasoning often leads to more accurate results.
Real-life examples
CoT Chain Thinking can also be found everywhere in daily life. For example, when we cook, we need to prepare the ingredients first, then cook them, and finally serve them. This is a typical CoT chain thinking process. For example, when we learn a new knowledge, we need to understand the basics first, and then learn the advanced content.
We can compare Chain-of-Thought to a jigsaw puzzle, where each piece represents an aspect of a problem, and only by connecting these pieces can we get a complete answer. For example, when we are learning a new knowledge, we can use Chain-of-Thought to establish the relationship between various knowledge points, so as to better understand and memorize the knowledge; when we are solving a problem, we can use Chain-of-Thought to break down the problem into multiple sub-problems, and then solve them step by step to finally get a complete solution.
advantages and disadvantages
chain-of-Thought (CoT) is a method of thinking that improves the efficiency and quality of thinking by breaking down the process of thinking into a series of organically linked steps. Its advantages include:
1. Helping people to better organize and control the flow of ideas for better problem solving.
2. To support continuous thinking and promote creative thinking.
3. By tracking the thinking process, the quality of thinking can be better checked and optimized.
4. Can be used to solve complex problems ranging from organization to innovation.
Disadvantages of CoT:
1. CoT requires a large knowledge base and analytical skills and is not suitable for beginners
2. CoT requires time and thought effort and is difficult to use under tight time constraints
3. Everyone's thinking patterns may be different, so CoT may not be the best way of thinking for different people.
Classification of COT methods
Least-to-Most (Less-to-More Tips)
CoT works well on easy problems, but not on hard problems. And Least-to-Most Prompting is mainly used to solve hard problems.
Least-to-Most Prompting
The Least-to-Most Prompting idea is also very simple, which is to break down the question into simpler sub-questions, and then answer the sub-questions one by one to finally get the answer to the original question:

In addition to the above trick, another trick is to add a small number of samples (few-shots) in the prompt, which can significantly improve the effect. This trick is also found in CoT, and is a very general way to improve results.
In the paper, the following two main prompt structures are designed for different tasks in the specific implementation (a small number of samples in the prompt are omitted):
1. Let's break down this problem.
This approach isinvoke onceLLM, so that it generates sub-problems first, and then generates the answer to each sub-problem, and the final answer. So it's largely up to the samples to standardize the output of the LLM.

2. To solve "****", we need to first solve: "****", "****", "****", .... subproblem2>**", "****", ...
This approach isiteration (math.)Generate answers to the sub-questions, summarize all the information and then generate the final answer.
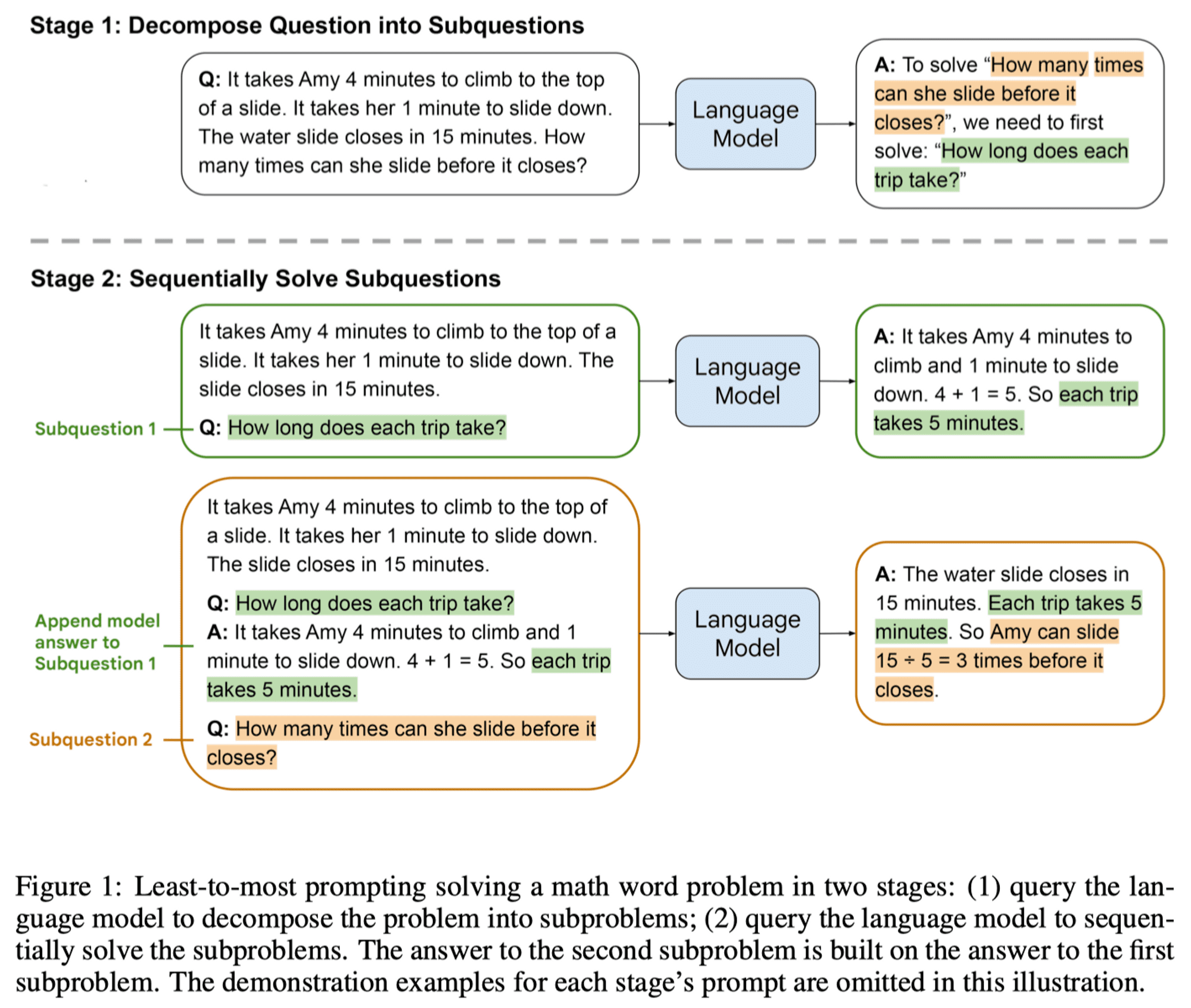
I understand that the specific cue words used by prompt (**break down** or **first solve**) are not important, what is important is thatBreak it down into subtasks firstonce againcase-by-case answerThe thought process.
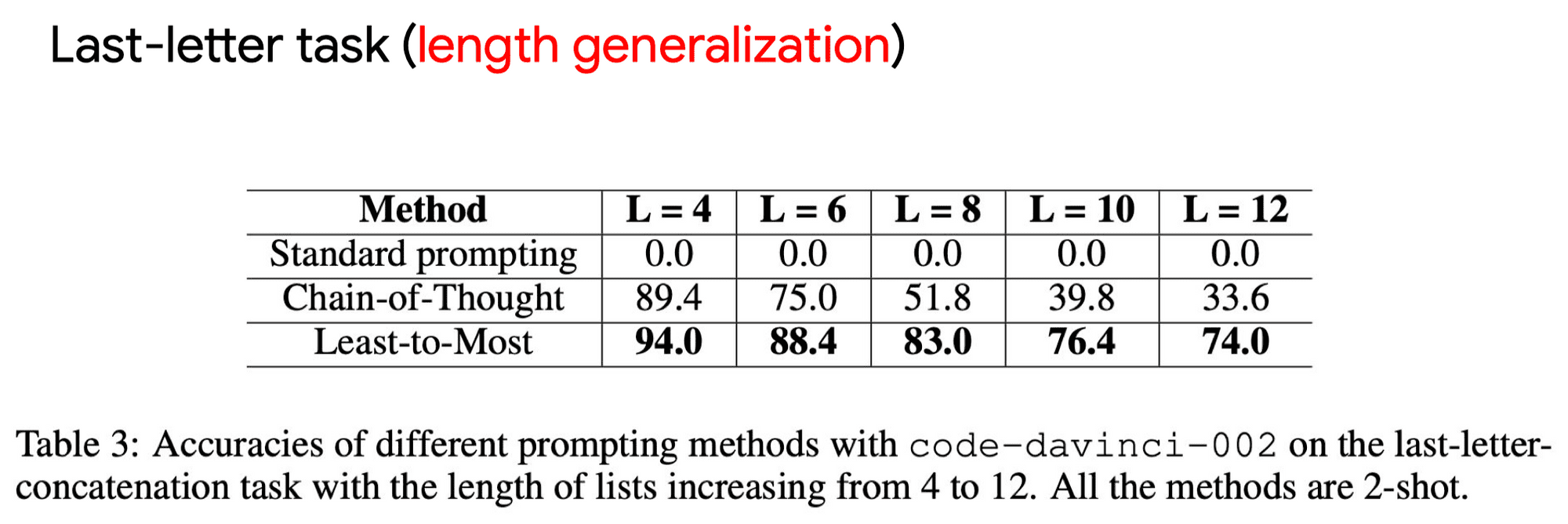
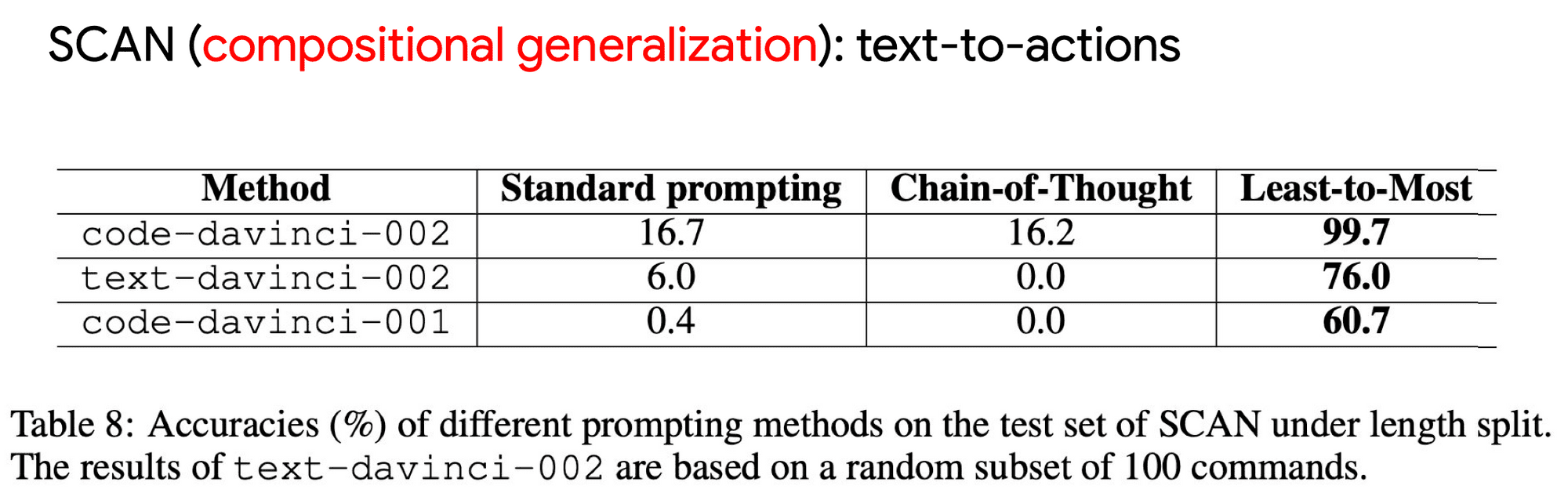
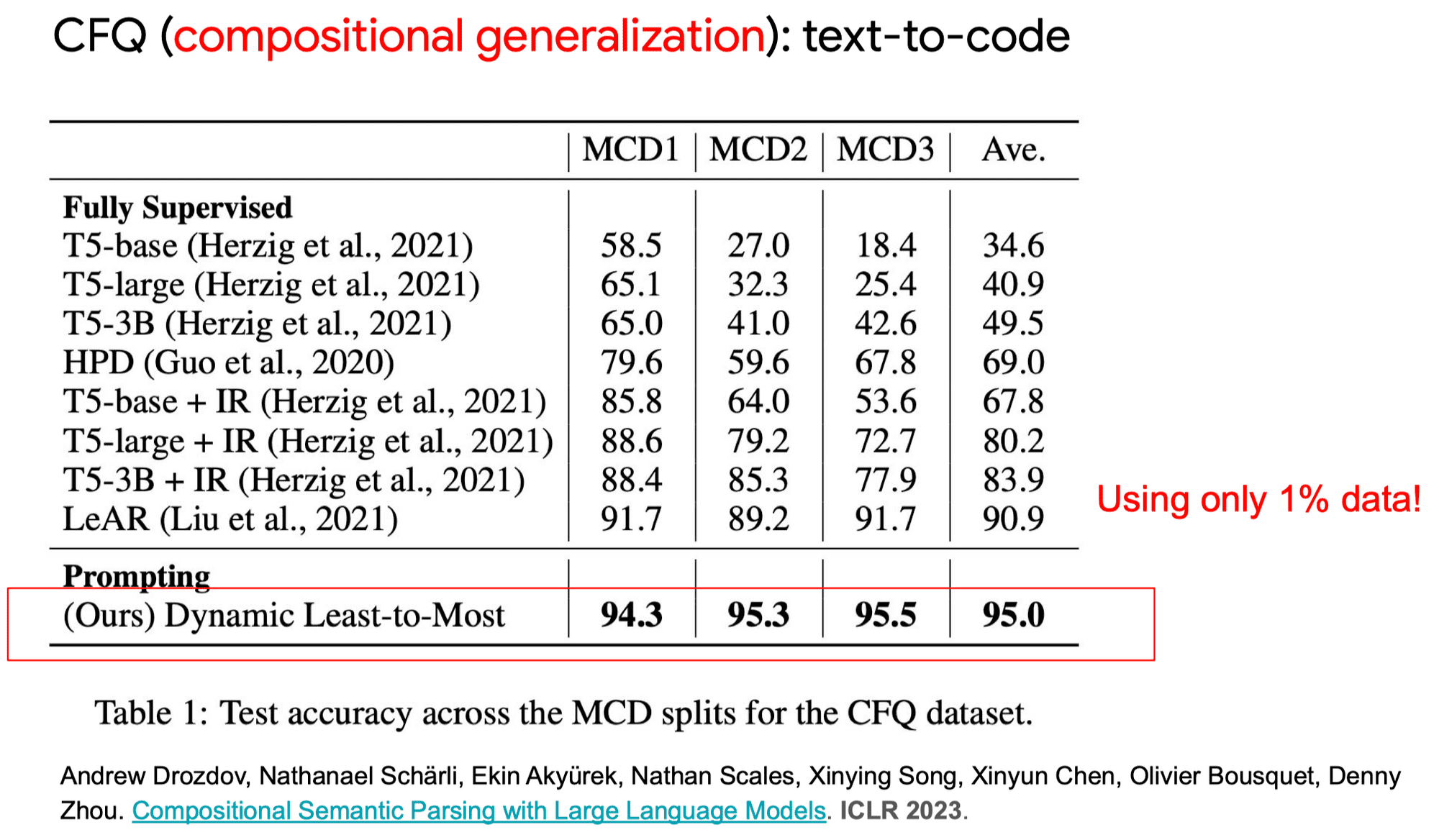
Effect:
© Copyright notes
Article copyright AI Sharing Circle All, please do not reproduce without permission.
Related articles

No comments...


![Sora视频生成模型:构建虚拟世界的模拟器 [译]](https://aisharenet.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/02/b29cc0bf0bfa1d3.png)

