cognee: un marco RAG de código abierto para la construcción basada en grafos de conocimiento, aprendizaje de prompts básicos
Últimos recursos sobre IAActualizado hace 1 año Círculo de intercambio de inteligencia artificial 75.8K 00
Introducción general
Cognee es una solución de capa de datos fiable diseñada para aplicaciones de IA y agentes de IA. Diseñado para cargar y construir contextos LLM (Large Language Models) para crear soluciones de IA precisas e interpretables a través de grafos de conocimiento y almacenes de vectores. El marco de trabajo facilita el ahorro de costes, la interpretabilidad y el control guiado por el usuario, lo que lo hace adecuado para la investigación y el uso educativo. El sitio web oficial ofrece tutoriales introductorios, panoramas conceptuales, material didáctico e información relacionada con la investigación.
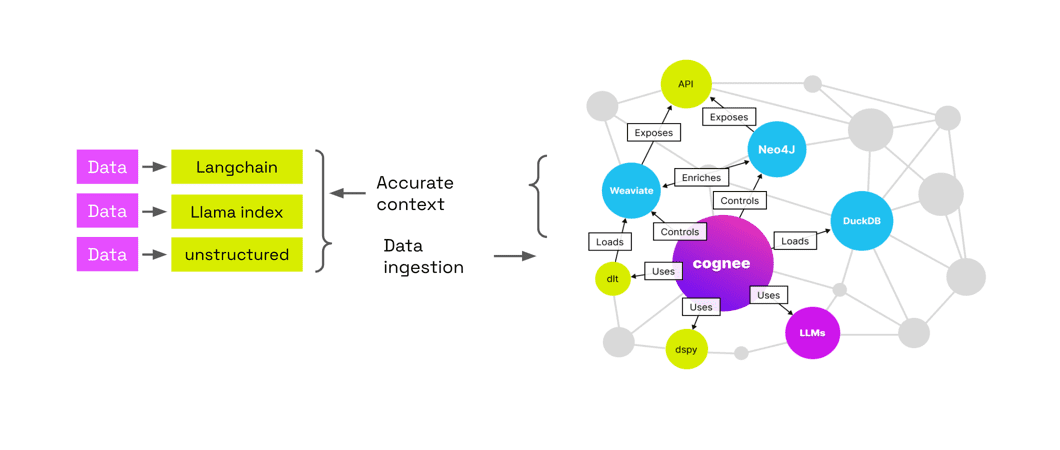
El mayor punto fuerte de cognee es arrojarle datos y luego procesarlos automáticamente y construir un gráfico de conocimiento y volver a conectar los gráficos de temas relacionados entre sí para ayudarte a descubrir mejor las conexiones en los datos, así como las RAG Ofrece lo último en interpretabilidad cuando se trata de LLM.
1. Añade datos, identifica y procesa automáticamente datos basados en LLM, extrae en Knowledge Graph y puede almacenar weaviate base de datos vectorial 2. Las ventajas son: ahorro de dinero, interpretabilidad (visualización gráfica de los datos), controlabilidad (integración en el código), etc.
Lista de funciones
- Tuberías ECL: Permite la extracción, la cognición y la carga de datos, admite la interconexión y la recuperación de datos históricos.
- Soporte multibase de datosSoporte para PostgreSQL, Weaviate, Qdrant, Neo4j, Milvus y otras bases de datos.
- Reducción de las alucinaciones: Reducción de fenómenos fantasma en aplicaciones de IA mediante la optimización del diseño de canalizaciones.
- Desarrolladores: Proporcionar documentación detallada y ejemplos para rebajar el umbral de los desarrolladores.
- escalabilidadDiseño modular para facilitar la ampliación y la personalización.
Utilizar la ayuda
Proceso de instalación
- Instalación mediante pip::
pip install cogneeO instalar un soporte de base de datos específico:
pip install 'cognee[<database>]'Por ejemplo, instale PostgreSQL y soporte Neo4j:
pip install 'cognee[postgres, neo4j]' - Instalación con poesía::
poetry add cogneeO instalar un soporte de base de datos específico:
poetry add cognee -E <database>Por ejemplo, instale PostgreSQL y soporte Neo4j:
poetry add cognee -E postgres -E neo4j
Proceso de utilización
- Configuración de la clave API::
import os os.environ["LLM_API_KEY"] = "YOUR_OPENAI_API_KEY"O:
import cognee cognee.config.set_llm_api_key("YOUR_OPENAI_API_KEY") - Creación de archivos .envCree un archivo .env y establezca la clave API:
LLM_API_KEY=YOUR_OPENAI_API_KEY - Utilizar diferentes proveedores de LLMConsulte la documentación para saber cómo configurar los distintos proveedores de LLM.
- Resultados de la visualizaciónSi utiliza Red, cree una cuenta Graphistry y configúrela:
cognee.config.set_graphistry_config({ "username": "YOUR_USERNAME", "password": "YOUR_PASSWORD" })
Funciones principales
- extracción de datosExtracción de datos mediante la canalización ECL de Cognee, que admite múltiples fuentes y formatos de datos.
- Conocimiento de los datos: Procesamiento y análisis de datos mediante el módulo cognitivo de Cognee para reducir las alucinaciones.
- Carga de datosCarga de datos procesados en una base de datos o almacén de destino, compatible con una amplia gama de bases de datos y almacenes de vectores.
Funciones destacadas Procedimiento de funcionamiento
- Interconexión y recuperación de datos históricosInterconexión y recuperación sencillas de conversaciones anteriores, documentos y transcripciones de audio gracias al diseño modular de Cognee.
- Reducción de la carga de trabajo de los desarrolladores: Proporcionar documentación detallada y ejemplos para rebajar el umbral de los desarrolladores y reducir el tiempo y los costes de desarrollo.
Visite el sitio web oficial para obtener más información sobre los marcos cognee
Lea un resumen del dominio de los fundamentos teóricos de cognee
Ver tutoriales y material didáctico para empezar
Comando Core prompt
classify_content: contenido clasificado
You are a classification engine and should classify content. Make sure to use one of the existing classification options nad not invent your own.
The possible classifications are:
{
"Natural Language Text": {
"type": "TEXT",
"subclass": [
"Articles, essays, and reports",
"Books and manuscripts",
"News stories and blog posts",
"Research papers and academic publications",
"Social media posts and comments",
"Website content and product descriptions",
"Personal narratives and stories"
]
},
"Structured Documents": {
"type": "TEXT",
"subclass": [
"Spreadsheets and tables",
"Forms and surveys",
"Databases and CSV files"
]
},
"Code and Scripts": {
"type": "TEXT",
"subclass": [
"Source code in various programming languages",
"Shell commands and scripts",
"Markup languages (HTML, XML)",
"Stylesheets (CSS) and configuration files (YAML, JSON, INI)"
]
},
"Conversational Data": {
"type": "TEXT",
"subclass": [
"Chat transcripts and messaging history",
"Customer service logs and interactions",
"Conversational AI training data"
]
},
"Educational Content": {
"type": "TEXT",
"subclass": [
"Textbook content and lecture notes",
"Exam questions and academic exercises",
"E-learning course materials"
]
},
"Creative Writing": {
"type": "TEXT",
"subclass": [
"Poetry and prose",
"Scripts for plays, movies, and television",
"Song lyrics"
]
},
"Technical Documentation": {
"type": "TEXT",
"subclass": [
"Manuals and user guides",
"Technical specifications and API documentation",
"Helpdesk articles and FAQs"
]
},
"Legal and Regulatory Documents": {
"type": "TEXT",
"subclass": [
"Contracts and agreements",
"Laws, regulations, and legal case documents",
"Policy documents and compliance materials"
]
},
"Medical and Scientific Texts": {
"type": "TEXT",
"subclass": [
"Clinical trial reports",
"Patient records and case notes",
"Scientific journal articles"
]
},
"Financial and Business Documents": {
"type": "TEXT",
"subclass": [
"Financial reports and statements",
"Business plans and proposals",
"Market research and analysis reports"
]
},
"Advertising and Marketing Materials": {
"type": "TEXT",
"subclass": [
"Ad copies and marketing slogans",
"Product catalogs and brochures",
"Press releases and promotional content"
]
},
"Emails and Correspondence": {
"type": "TEXT",
"subclass": [
"Professional and formal correspondence",
"Personal emails and letters"
]
},
"Metadata and Annotations": {
"type": "TEXT",
"subclass": [
"Image and video captions",
"Annotations and metadata for various media"
]
},
"Language Learning Materials": {
"type": "TEXT",
"subclass": [
"Vocabulary lists and grammar rules",
"Language exercises and quizzes"
]
},
"Audio Content": {
"type": "AUDIO",
"subclass": [
"Music tracks and albums",
"Podcasts and radio broadcasts",
"Audiobooks and audio guides",
"Recorded interviews and speeches",
"Sound effects and ambient sounds"
]
},
"Image Content": {
"type": "IMAGE",
"subclass": [
"Photographs and digital images",
"Illustrations, diagrams, and charts",
"Infographics and visual data representations",
"Artwork and paintings",
"Screenshots and graphical user interfaces"
]
},
"Video Content": {
"type": "VIDEO",
"subclass": [
"Movies and short films",
"Documentaries and educational videos",
"Video tutorials and how-to guides",
"Animated features and cartoons",
"Live event recordings and sports broadcasts"
]
},
"Multimedia Content": {
"type": "MULTIMEDIA",
"subclass": [
"Interactive web content and games",
"Virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) experiences",
"Mixed media presentations and slide decks",
"E-learning modules with integrated multimedia",
"Digital exhibitions and virtual tours"
]
},
"3D Models and CAD Content": {
"type": "3D_MODEL",
"subclass": [
"Architectural renderings and building plans",
"Product design models and prototypes",
"3D animations and character models",
"Scientific simulations and visualizations",
"Virtual objects for AR/VR environments"
]
},
"Procedural Content": {
"type": "PROCEDURAL",
"subclass": [
"Tutorials and step-by-step guides",
"Workflow and process descriptions",
"Simulation and training exercises",
"Recipes and crafting instructions"
]
}
}
generate_cog_layers: generar capas cognitivas
You are tasked with analyzing `{{ data_type }}` files, especially in a multilayer network context for tasks such as analysis, categorization, and feature extraction. Various layers can be incorporated to capture the depth and breadth of information contained within the {{ data_type }}.
These layers can help in understanding the content, context, and characteristics of the `{{ data_type }}`.
Your objective is to extract meaningful layers of information that will contribute to constructing a detailed multilayer network or knowledge graph.
Approach this task by considering the unique characteristics and inherent properties of the data at hand.
VERY IMPORTANT: The context you are working in is `{{ category_name }}` and the specific domain you are extracting data on is `{{ category_name }}`.
Guidelines for Layer Extraction:
Take into account: The content type, in this case, is: `{{ category_name }}`, should play a major role in how you decompose into layers.
Based on your analysis, define and describe the layers you've identified, explaining their relevance and contribution to understanding the dataset. Your independent identification of layers will enable a nuanced and multifaceted representation of the data, enhancing applications in knowledge discovery, content analysis, and information retrieval.
generate_graph_prompt: generar avisos gráficos
You are a top-tier algorithm
designed for extracting information in structured formats to build a knowledge graph.
- **Nodes** represent entities and concepts. They're akin to Wikipedia nodes.
- **Edges** represent relationships between concepts. They're akin to Wikipedia links.
- The aim is to achieve simplicity and clarity in the
knowledge graph, making it accessible for a vast audience.
YOU ARE ONLY EXTRACTING DATA FOR COGNITIVE LAYER `{{ layer }}`
## 1. Labeling Nodes
- **Consistency**: Ensure you use basic or elementary types for node labels.
- For example, when you identify an entity representing a person,
always label it as **"Person"**.
Avoid using more specific terms like "mathematician" or "scientist".
- Include event, entity, time, or action nodes to the category.
- Classify the memory type as episodic or semantic.
- **Node IDs**: Never utilize integers as node IDs.
Node IDs should be names or human-readable identifiers found in the text.
## 2. Handling Numerical Data and Dates
- Numerical data, like age or other related information,
should be incorporated as attributes or properties of the respective nodes.
- **No Separate Nodes for Dates/Numbers**:
Do not create separate nodes for dates or numerical values.
Always attach them as attributes or properties of nodes.
- **Property Format**: Properties must be in a key-value format.
- **Quotation Marks**: Never use escaped single or double quotes within property values.
- **Naming Convention**: Use snake_case for relationship names, e.g., `acted_in`.
## 3. Coreference Resolution
- **Maintain Entity Consistency**:
When extracting entities, it's vital to ensure consistency.
If an entity, such as "John Doe", is mentioned multiple times
in the text but is referred to by different names or pronouns (e.g., "Joe", "he"),
always use the most complete identifier for that entity throughout the knowledge graph.
In this example, use "John Doe" as the entity ID.
Remember, the knowledge graph should be coherent and easily understandable,
so maintaining consistency in entity references is crucial.
## 4. Strict Compliance
Adhere to the rules strictly. Non-compliance will result in termination"""
read_query_prompt: consulta de lectura
from os import path
import logging
from cognee.root_dir import get_absolute_path
def read_query_prompt(prompt_file_name: str):
"""Read a query prompt from a file."""
try:
file_path = path.join(get_absolute_path("./infrastructure/llm/prompts"), prompt_file_name)
with open(file_path, "r", encoding = "utf-8") as file:
return file.read()
except FileNotFoundError:
logging.error(f"Error: Prompt file not found. Attempted to read: %s {file_path}")
return None
except Exception as e:
logging.error(f"An error occurred: %s {e}")
return None
render_prompt: aviso de renderizado
from jinja2 import Environment, FileSystemLoader, select_autoescape
from cognee.root_dir import get_absolute_path
def render_prompt(filename: str, context: dict) -> str:
"""Render a Jinja2 template asynchronously.
:param filename: The name of the template file to render.
:param context: The context to render the template with.
:return: The rendered template as a string."""
# Set the base directory relative to the cognee root directory
base_directory = get_absolute_path("./infrastructure/llm/prompts")
# Initialize the Jinja2 environment to load templates from the filesystem
env = Environment(
loader = FileSystemLoader(base_directory),
autoescape = select_autoescape(["html", "xml", "txt"])
)
# Load the template by name
template = env.get_template(filename)
# Render the template with the provided context
rendered_template = template.render(context)
return rendered_template
summarize_content: contenido resumido
You are a summarization engine and you should sumamarize content. Be brief and concise
© declaración de copyright
Derechos de autor del artículo Círculo de intercambio de inteligencia artificial Todos, por favor no reproducir sin permiso.
Artículos relacionados

Sin comentarios...