Microsoft Getting Started with AI Agents: An Overview of AI Agents in Production Environments
summary
This course will cover:
- How to effectively plan for the deployment of an AI Agent into a production environment.
- Common errors and problems you may encounter when deploying AI Agent to a production environment.
- How to manage costs while maintaining AI Agent performance.
Learning Objectives
Upon completion of this course, you will know how to/understand:
- Techniques for improving the performance, cost, and effectiveness of AI Agent systems for production environments.
- Evaluate the content and methods of AI Agents.
- How to control costs when deploying AI Agents to a production environment.
Deploying trusted AI Agents is important. Also check out the Building Trusted AI Agents course.
Evaluating AI Agents
It is critical to have a proper system for evaluating AI Agents before, during, and after they are deployed. This will ensure that your system is aligned with your goals and those of your users.
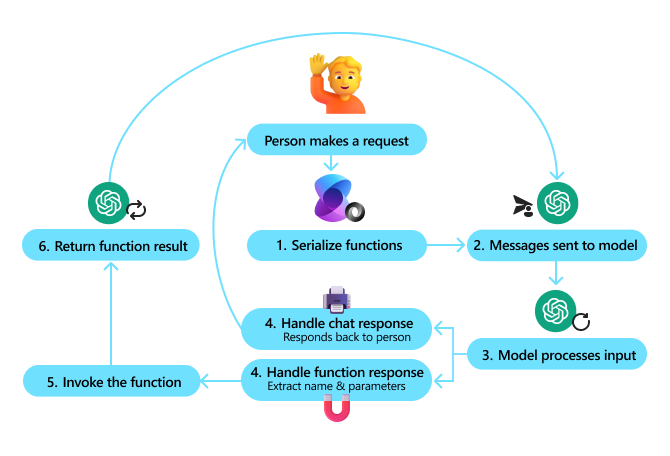
To evaluate an AI Agent, it is important to evaluate not only the output of the Agent, but also the entire system in which the AI Agent is running. This includes, but is not limited to:
- Initial model request.
- Agent's ability to recognize user intent.
- Agent's ability to recognize the correct tool for performing a task.
- The tool's response to an Agent request.
- Agent's ability to interpret tool responses.
- User feedback on Agent responses.
This allows you to identify areas for improvement in a more modular way. You can then more effectively monitor the effects of changes to models, hints, tools, and other components.
Common Problems and Potential Solutions for AI Agents
| concern | Potential solutions |
|---|---|
| AI Agent fails to perform tasks consistently | - Improve cues to AI Agents; clarify goals. - Determine where it would be helpful to divide tasks into subtasks and have them handled by multiple Agents. |
| The AI Agent is caught in a continuous loop. | - Make sure you have clear termination terms and conditions so that the Agent knows when to stop the process. - For complex tasks that require reasoning and planning, use larger models that are specialized for reasoning tasks. |
| Poor AI Agent tool invocation | - Test and validate tool output outside the Agent system. - Improved defined parameters, hints and tool naming. |
| Multi-agent systems fail to perform consistently | - Improve the hints given to each Agent to make sure they are specific and different from each other. - Build a hierarchical system using "Route" or Controller Agents to determine which Agent is the correct one. |
management costs
Here are some strategies for managing the cost of deploying AI Agents to a production environment:
- Cache Response - Recognizing common requests and tasks and providing responses before they pass through your Agent system is a great way to reduce the volume of similar requests. You can even use more basic AI models to implement a process to recognize how similar a request is to a cached request.
- Use of smaller models - Small Language Models (SLMs) can perform well in some Agent use cases and will significantly reduce costs. As mentioned earlier, building an evaluation system to determine and compare performance with larger models is the best way to understand how SLMs will perform in your use cases.
- Using the router model - A similar strategy is to use a variety of models and sizes. You can use large language models/small language models or serverless features to route requests to the most appropriate model based on complexity. This also helps reduce costs while ensuring performance for the right tasks.
congratulations
This is the last lesson of "AI Agents for Beginners".
We plan to continue to add courses based on feedback and changes in this growing industry, so please visit again in the near future.
© Copyright notes
Article copyright AI Sharing Circle All, please do not reproduce without permission.
Related articles

No comments...