Self-contained outpatient orientation workflow (chatflow) in Dify
Note: This article uses Dify v0.7.2.
This chat flow shows how to build a chatbot for outpatient guidance that can collect patient data via web or voice dialog. Simply understood, this means that the patient is given a recommendation for a department based on the patient's information (age, gender, and symptoms).
I. Workflow ideas
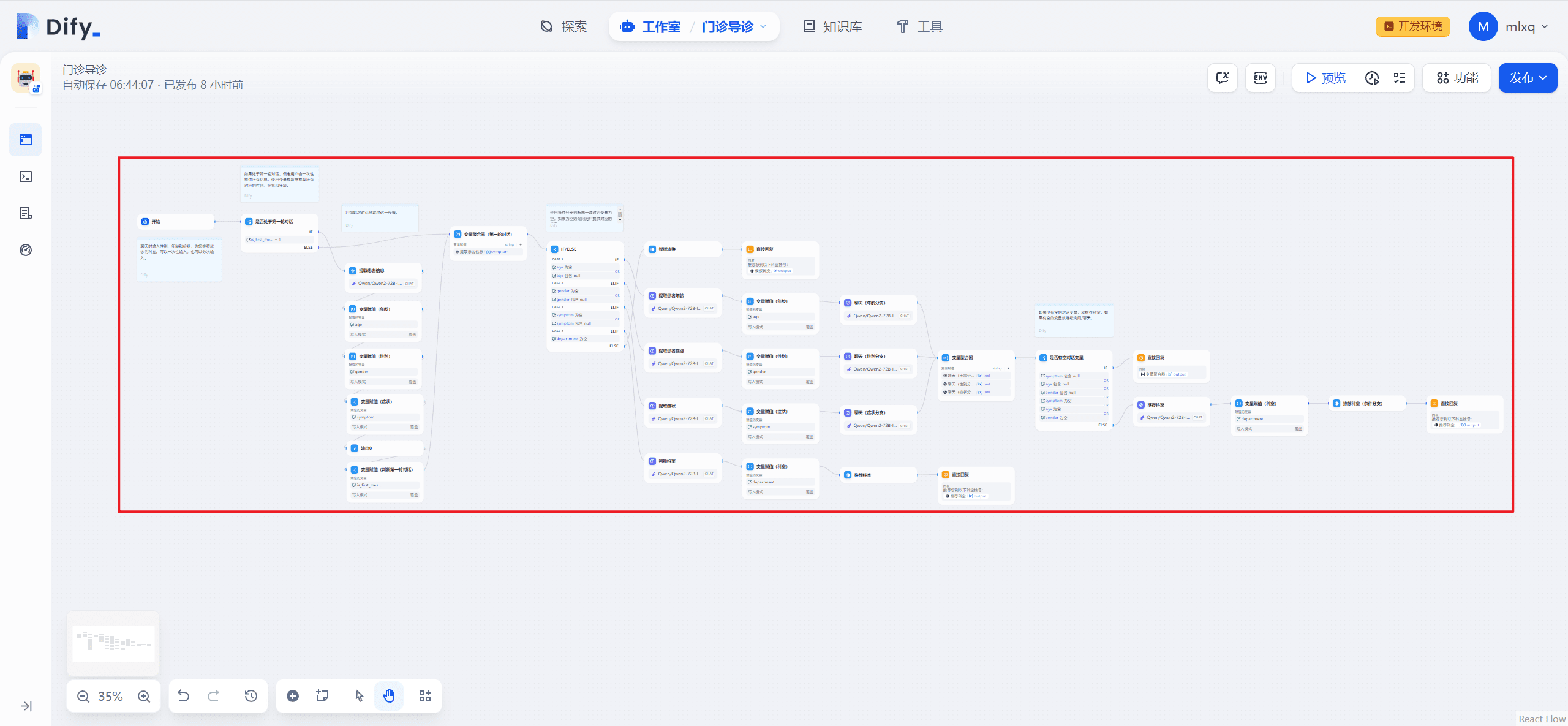
1. Workflow Screenshot
Screenshot of the complete workflow of the outpatient orientation, shown below:
2. Workflow pseudo-flowchart
The purpose of the outpatient guidance workflow is to recommend a department to a patient based on the patient's input of age, gender and symptoms. In the first round of dialog, since the patient may enter all or part of the information at once, the "Parameter Extractor" node is used to extract the gender, symptom and age from the patient's first input. The variable is_first_message is set to 0 by the "Variable Assignment" node.
3. Problems 1
During subsequent rounds of conversation, only 1 type of field information is recognized at a time, although the patient may provide multiple fields, with the order of field recognition being age, gender, and symptoms.
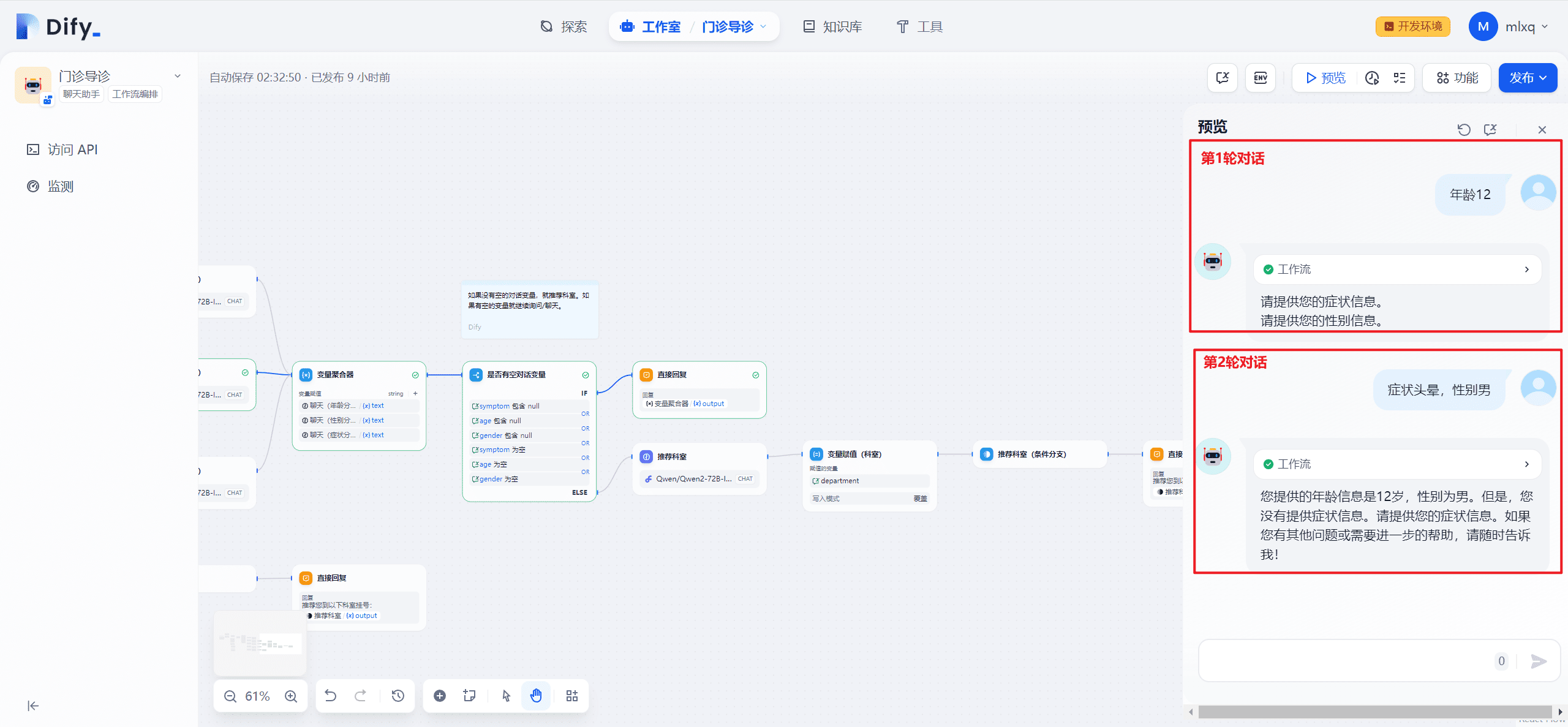
4. Problems 2
If a department has already been recommended based on patient information, then entering any information again will recommend the last department. Because the department field is not empty, the direct response process is followed.

II. Session variables
The session variable is used to store contextual information needed by LLM, such as user preferences, conversation history, etc. It is read-write. Session variables are oriented to multi-round conversation scenarios, so they are only available for Chatflow type (Chat Assistant -> Workflow Orchestration) applications.
1.session variabledata type
(1) String
(2) Number
(3) Object
(4) Array[string] Array of strings
(5) Array[number] Array of numbers
(6) Array[object] Array of objects
2.session variablecharacterization
(1) Session variables can be globally referenced within most nodes;
(2) Writing session variables requires the use of thevariable assignmentNodes;
(3) Session variables are read-write.
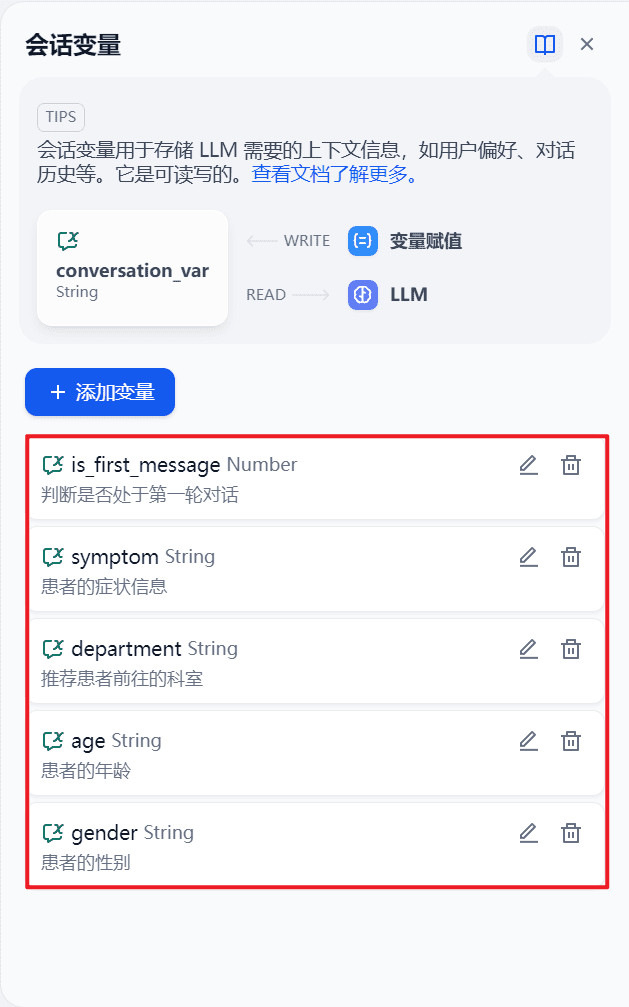
3. Session variables defined for this workflow
The five session variables defined for this workflow are whether it is the first round of conversation, age, gender, symptoms and department.
III. Workflow-related interfaces
1. Get the interface to the workflow
(1) Source code location
- Source code location: dedify-0.7.2\api\controllers\console\app\workflow.py
- Source code location: dedify-0.7.2\api\services\workflow_service.py
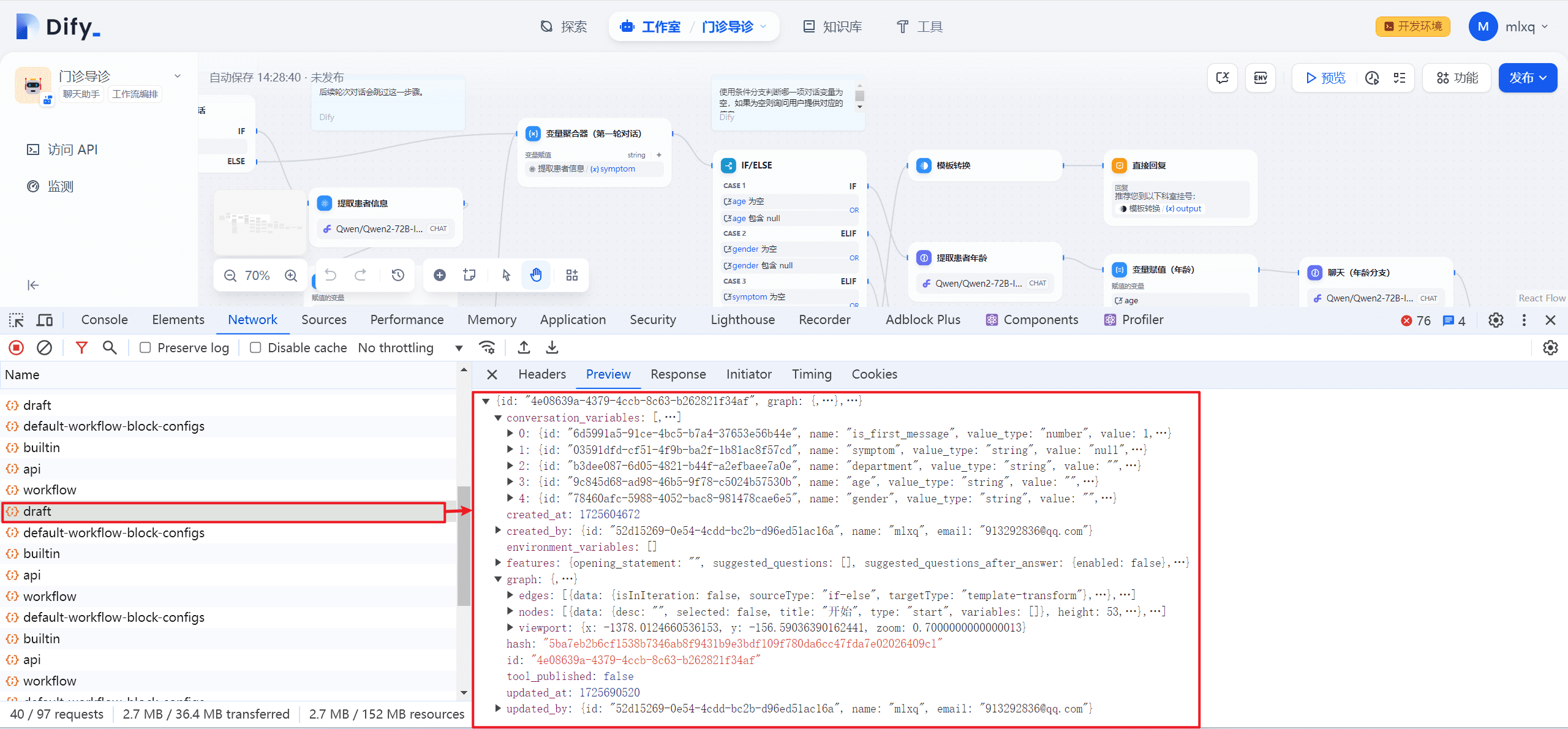
(2) Getting workflow operations
http://localhost:5001/console/api/apps/3c309371-54f6-4bfb-894a-4193b189ffa5/workflows/draft. where draft, like draft, indicates debugging in the workflow page.
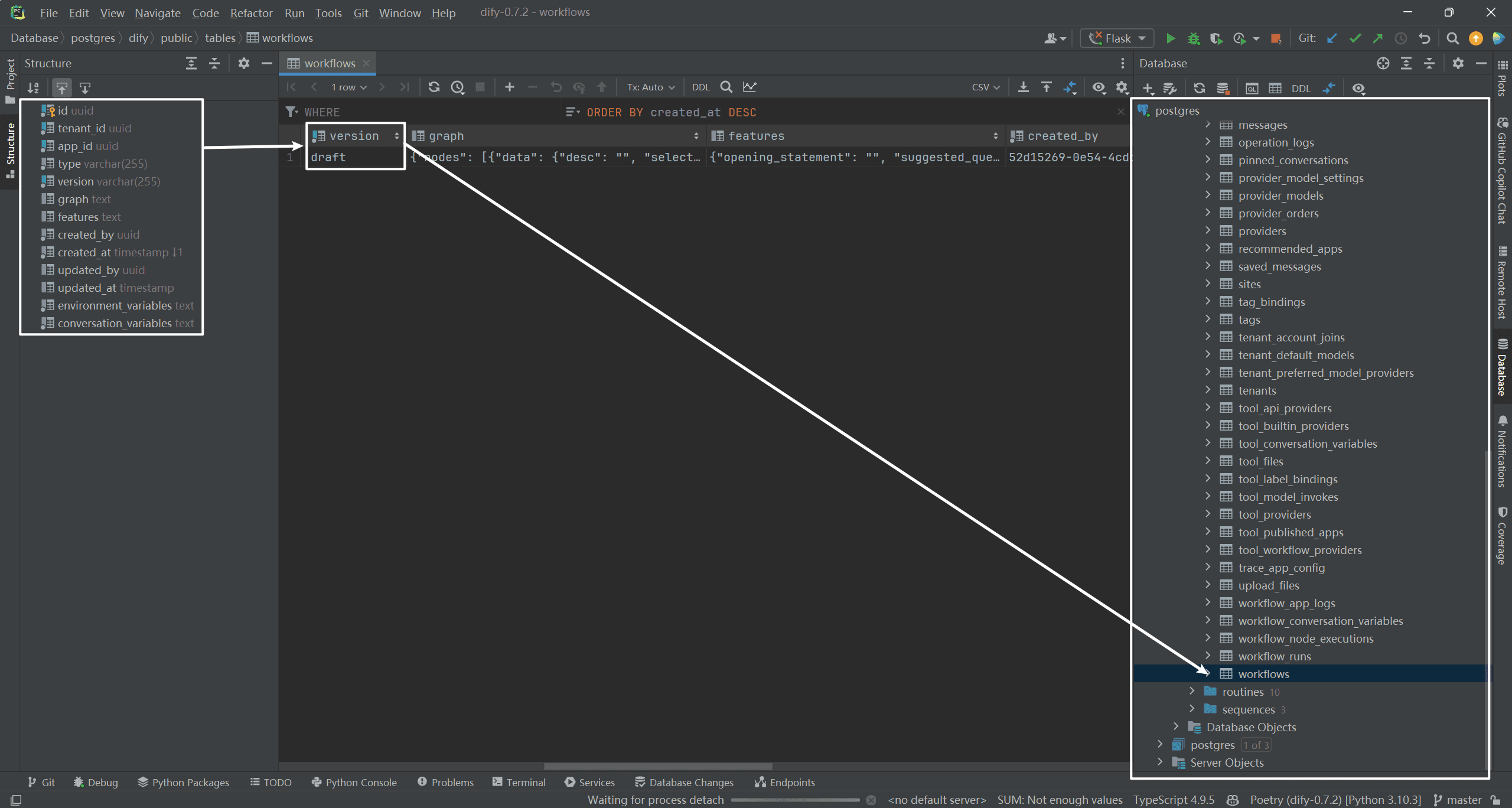
(3) Acquisition of workflow implementations
The workflow stores a record in the workflows data table. The version is now draft and every time a workflow is published, a record is inserted in that table. As shown below:
(4) Workflow data structure
The Workflow data structure returned by the interface is shown below:
class Workflow(db.Model):
__tablename__ = 'workflows'
__table_args__ = (
db.PrimaryKeyConstraint('id', name='workflow_pkey'),
db.Index('workflow_version_idx', 'tenant_id', 'app_id', 'version'),
)
id: Mapped[str] = db.Column(StringUUID, server_default=db.text('uuid_generate_v4()'))
tenant_id: Mapped[str] = db.Column(StringUUID, nullable=False)
app_id: Mapped[str] = db.Column(StringUUID, nullable=False)
type: Mapped[str] = db.Column(db.String(255), nullable=False)
version: Mapped[str] = db.Column(db.String(255), nullable=False)
graph: Mapped[str] = db.Column(db.Text)
features: Mapped[str] = db.Column(db.Text)
created_by: Mapped[str] = db.Column(StringUUID, nullable=False)
created_at: Mapped[datetime] = db.Column(db.DateTime, nullable=False, server_default=db.text('CURRENT_TIMESTAMP(0)'))
updated_by: Mapped[str] = db.Column(StringUUID)
updated_at: Mapped[datetime] = db.Column(db.DateTime)
_environment_variables: Mapped[str] = db.Column('environment_variables', db.Text, nullable=False, server_default='{}')
_conversation_variables: Mapped[str] = db.Column('conversation_variables', db.Text, nullable=False, server_default='{}')
2. Update workflow interfaces
(1) Source code location
- Source Location: dedify-0.7.2\web\app\components\workflow\hooks\use-nodes-sync-draft.ts
- Source Location: dedify-0.7.2\web\service\workflow.ts
(2) Update workflow operations
http://localhost:5001/console/api/apps/3c309371-54f6-4bfb-894a-4193b189ffa5/workflows/draft.
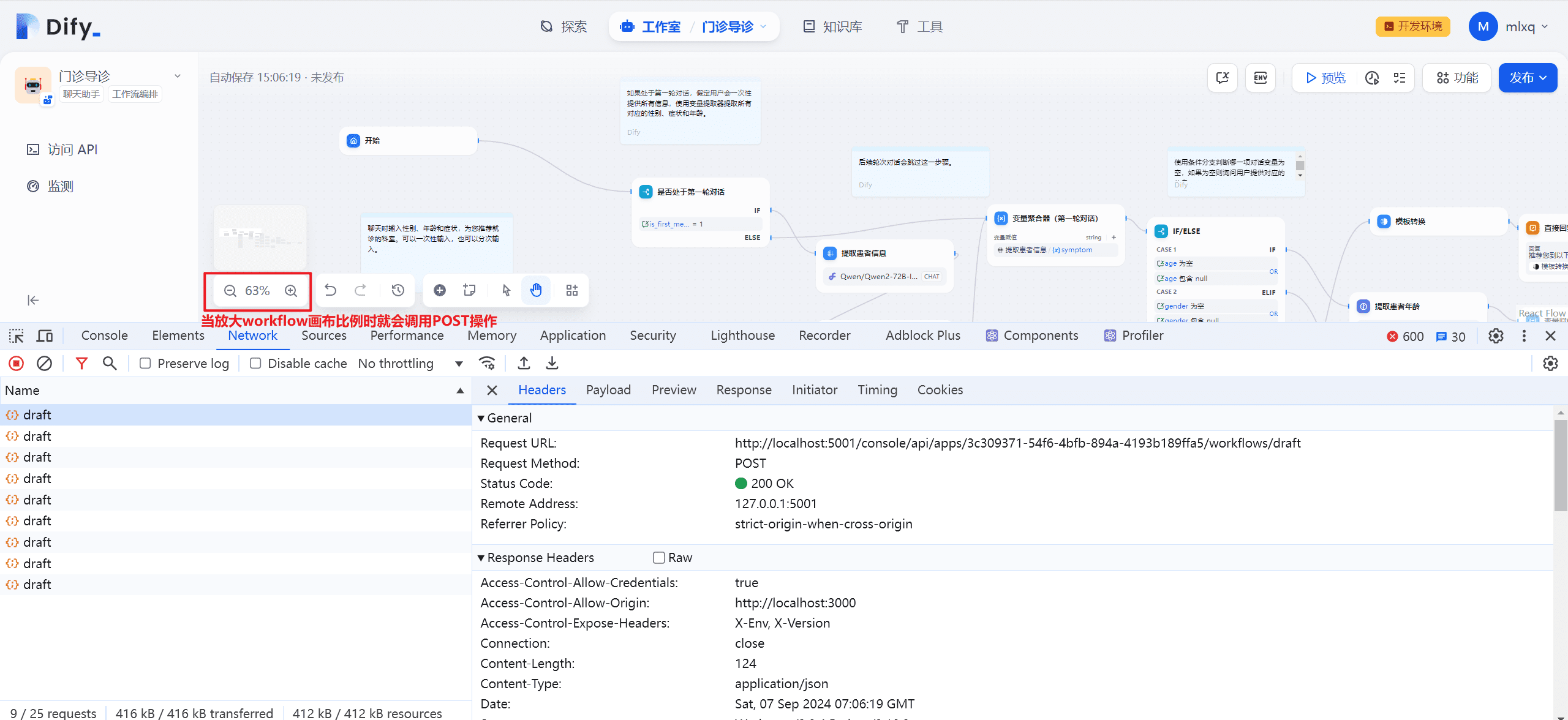
(3) Update workflow front-end code
Due to the React Flow framework used in the front-end of the Dify workflow, it is presumed that POST operations, such as add, delete, and change, may be performed when the workflow changes. Through the logs in the Console of the back-end, it was found that the call to theworkflows/draft?_token=::
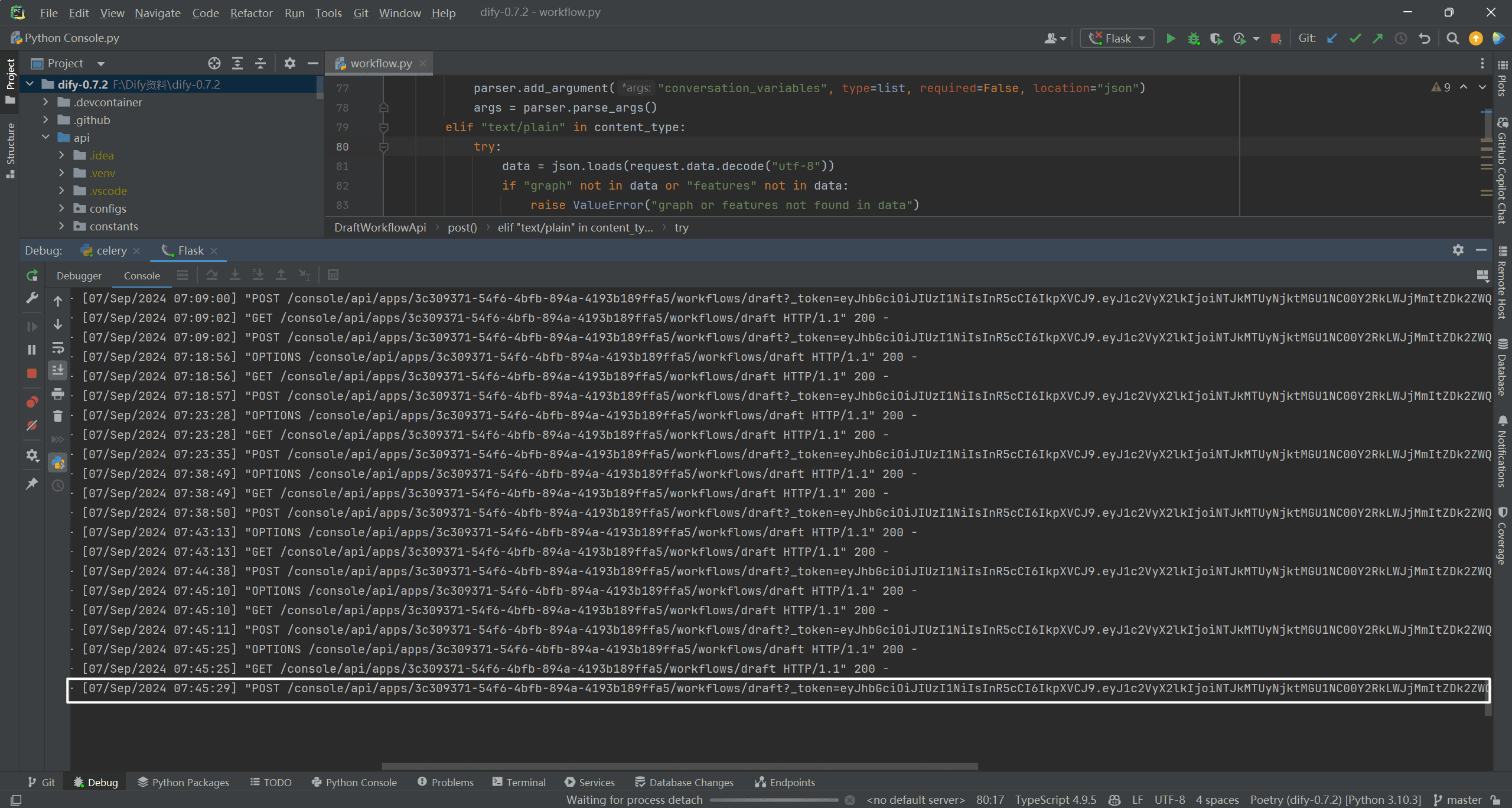
pass (a bill or inspection etc)workflows/draft?_token=Searching through the front-end code found only one place to use it, and that must be here.
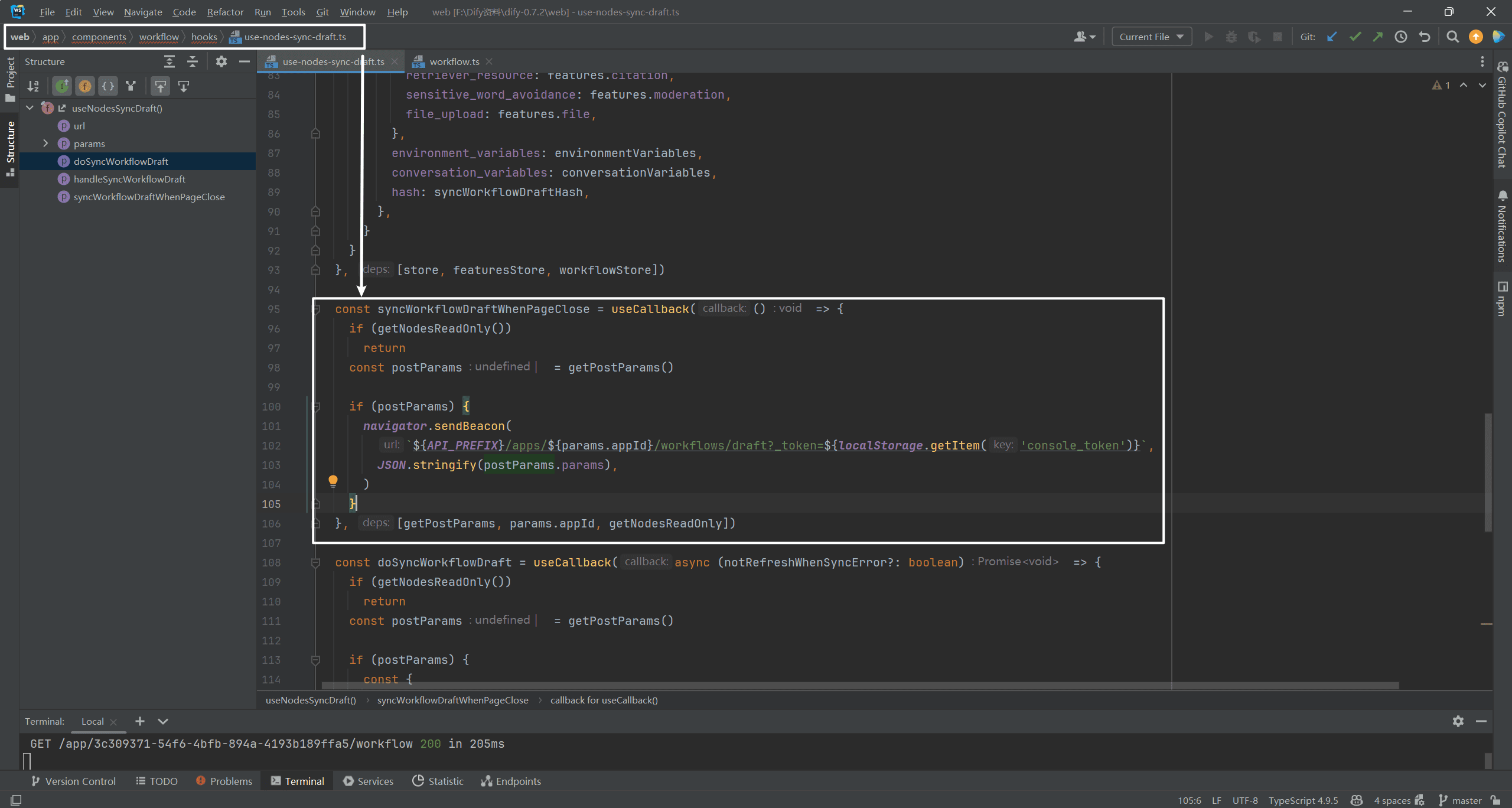
Since the POST operation is performed, there must be a Payload parameter, right, and the workflow parameter was found in that file.
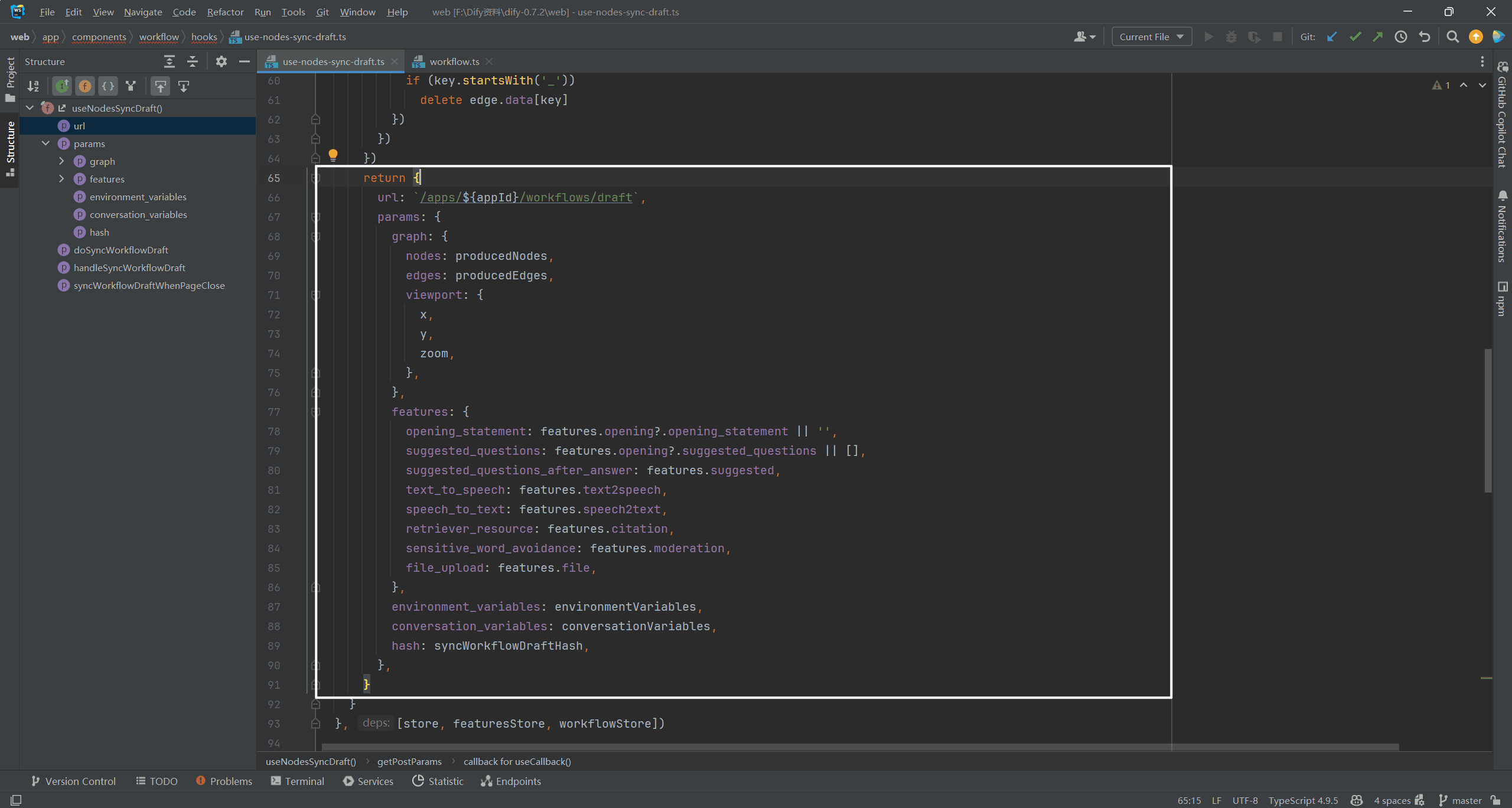
When the dependencygetPostParamsWhen a change occurs, it is executed asynchronouslysyncWorkflowDraft(postParams)The
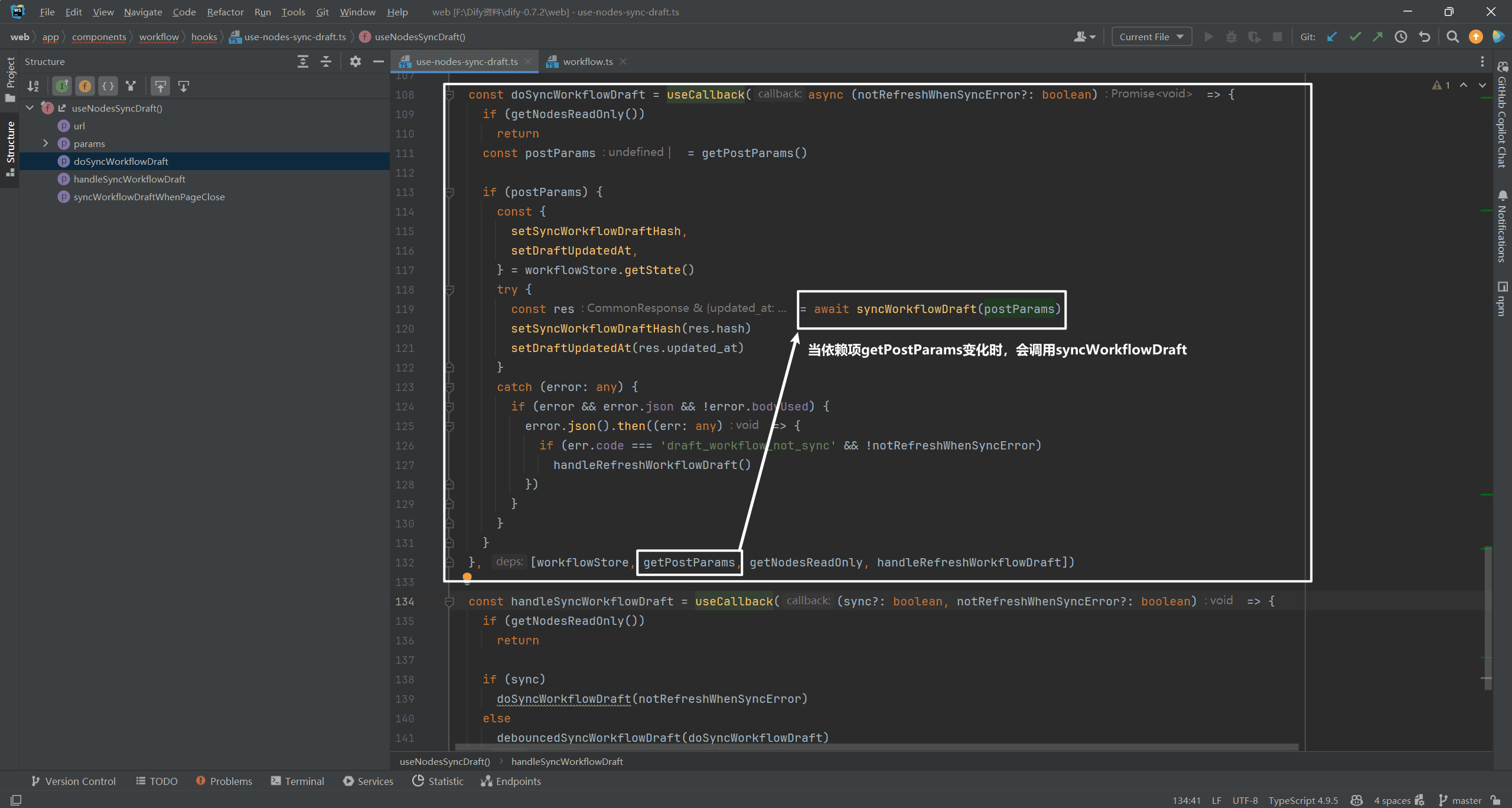
(indicates contrast)syncWorkflowDraft(postParams)The actual call is POST. as shown below:
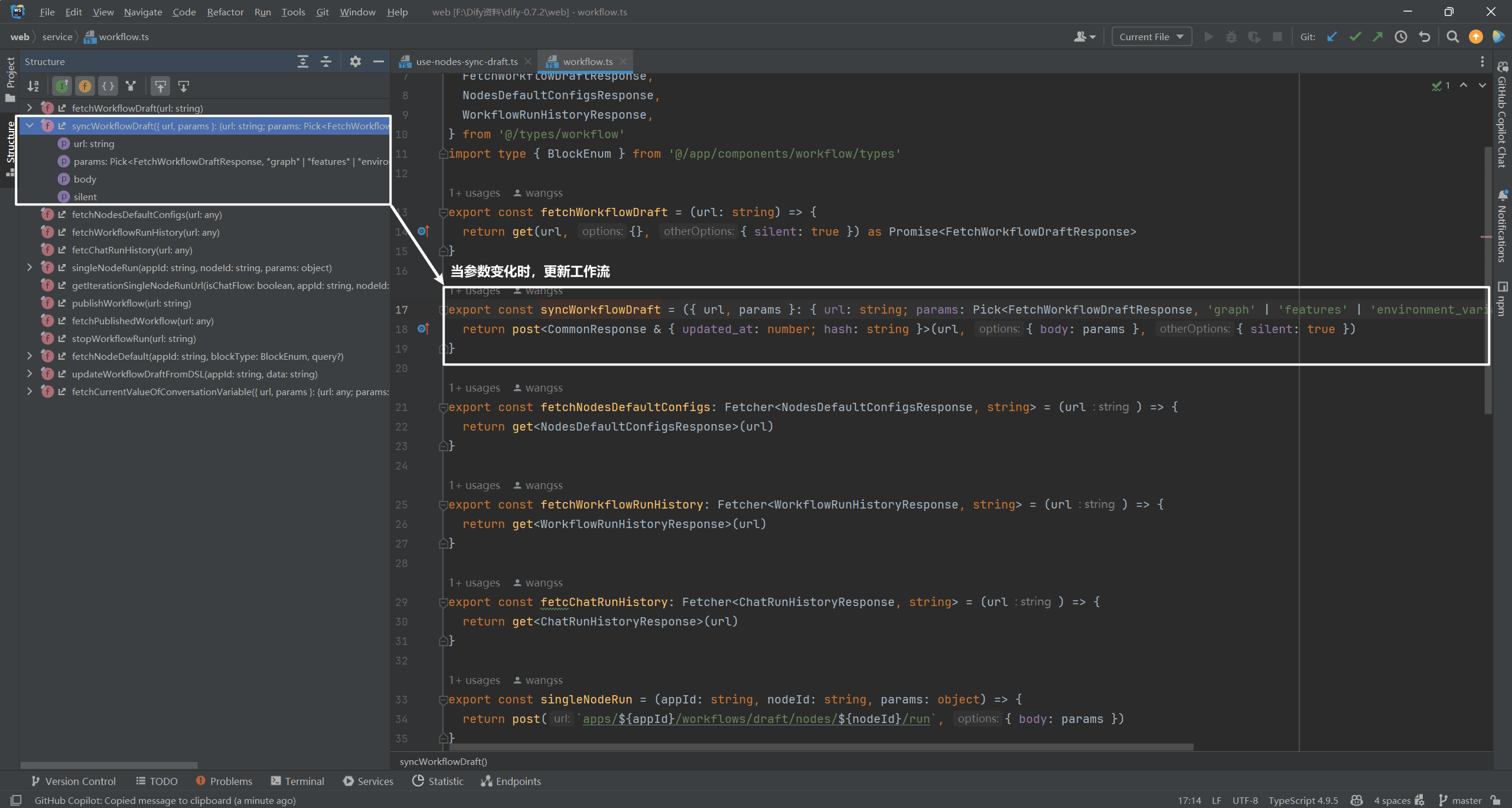
(4) Summary of workflow functions
rightdify-0.7.2\web\service\workflow.tsThe functions in are summarized as follows:
| serial number | function name | function function | Parameters and explanations |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | fetchWorkflowDraft | Get the draft workflow. | url: String, the URL of the request. |
| 2 | syncWorkflowDraft | Synchronize workflow drafts. | url: String, the URL of the request.params: object, the parameters of the request, containing the graph,features,environment_variables cap (a poem) conversation_variablesThe |
| 3 | fetchNodesDefaultConfigs | Get the default configuration of the node. | url: String, the URL of the request. |
| 4 | fetchWorkflowRunHistory | Get workflow run history. | url: String, the URL of the request. |
| 5 | fetcChatRunHistory | Get chat run history. | url: String, the URL of the request. |
| 6 | singleNodeRun | Run a single node. | appId: String, the ID of the application.nodeId: String, the ID of the node.params: Object, parameters of the request. |
| 7 | getIterationSingleNodeRunUrl | Gets the URL of the iteration run for a single node. | isChatFlow: Boolean value indicating whether the chat stream is a chat stream or not.appId: String, the ID of the application.nodeId: String, the ID of the node. |
| 8 | publishWorkflow | Post a workflow. | url: String, the URL of the request. |
| 9 | fetchPublishedWorkflow | Get published workflows. | url: String, the URL of the request. |
| 10 | stopWorkflowRun | Stop the workflow from running. | url: String, the URL of the request. |
| 11 | fetchNodeDefault | Get the default configuration of the node. | appId: String, the ID of the application.blockType: Enumeration value, type of node.query: Object, optional, query parameter. |
| 12 | updateWorkflowDraftFromDSL | Update workflow drafts from DSL. | appId: String, the ID of the application.data: String, DSL data. |
| 13 | fetchCurrentValueOfConversationVariable | Gets the current value of the session variable. | url: String, the URL of the request.params: object, the parameters of the request, containing the conversation_idThe |
3. Workflow implementation
Reference to theProcess implementation of Chatflow create, update, execute and delete operationsThe "Chatflow Implementation" section in [6].
4. Workflow publishing
(1) Source code location
- Source code location: dedify-0.7.2\api\controllers\console\app\workflow.py
- Source code location: dedify-0.7.2\api\services\workflow_service.py
- Source location: dedify-0.7.2\api\events\event_handlers\update_app_dataset_join_when_app_published_workflow_updated.py
(2) Workflow publishing interface
This is executed when you click Publish Workflowhttp://localhost:5001/console/api/apps/3c309371-54f6-4bfb-894a-4193b189ffa5/workflows/publishInterface.
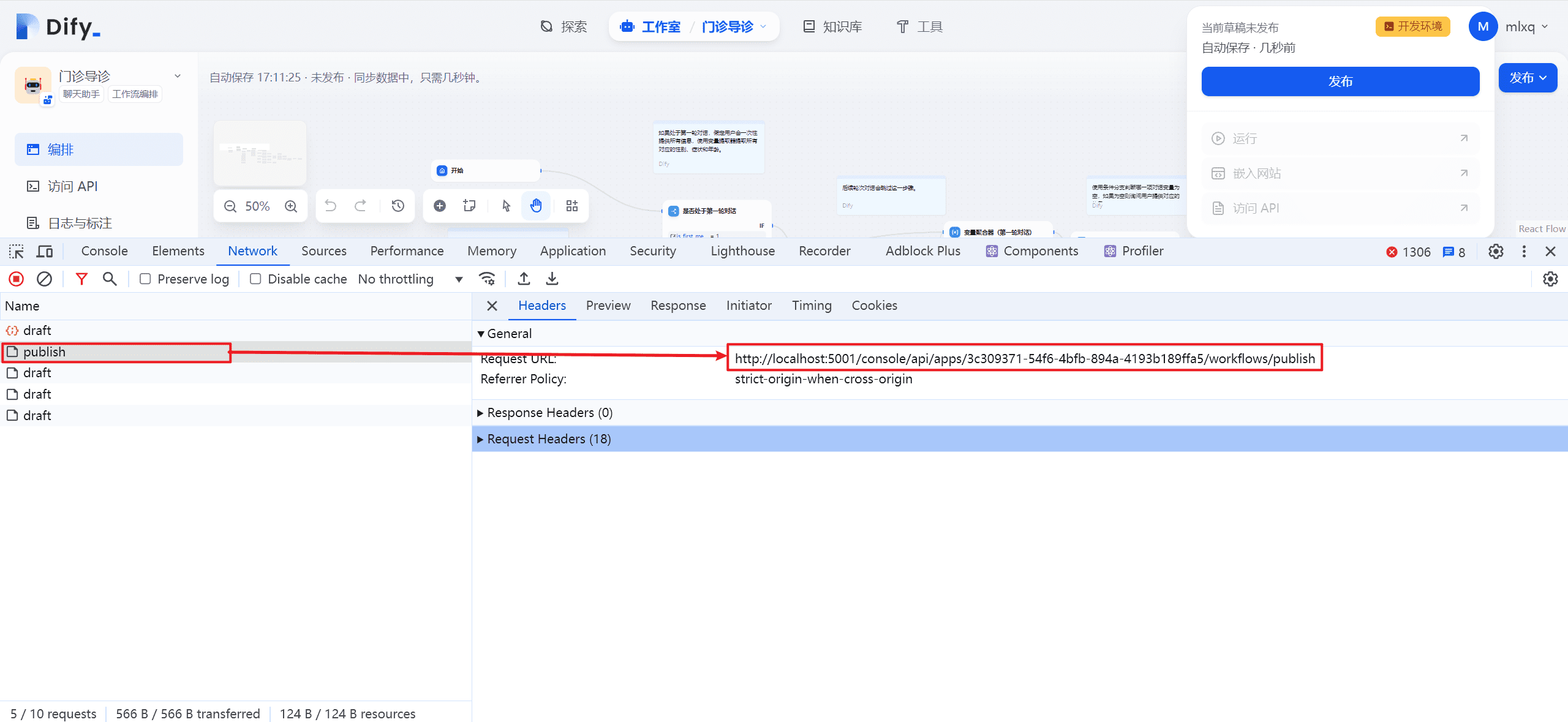
It mainly consists of creating a new workflow and triggering the app workflow event. As shown below:
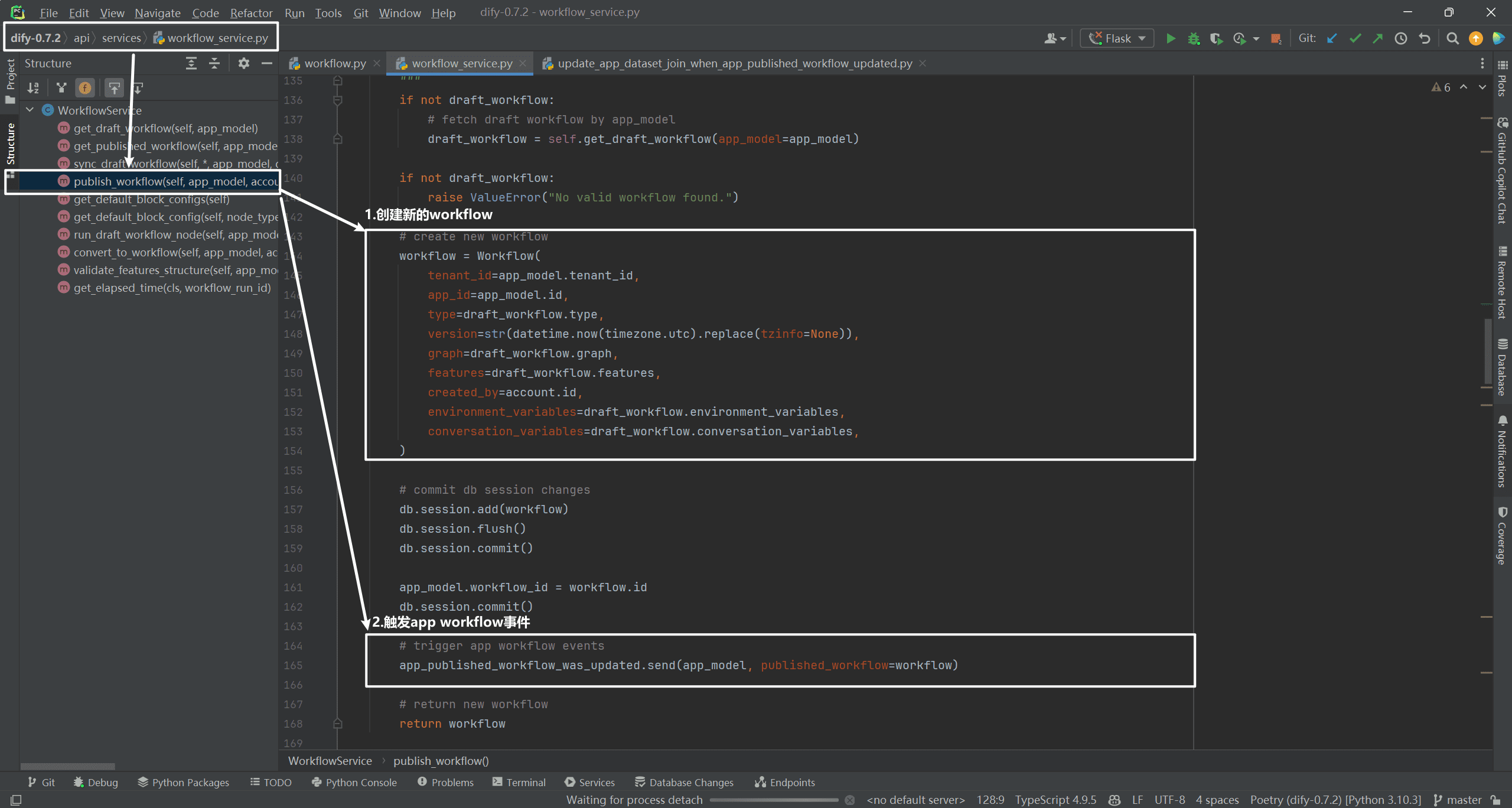
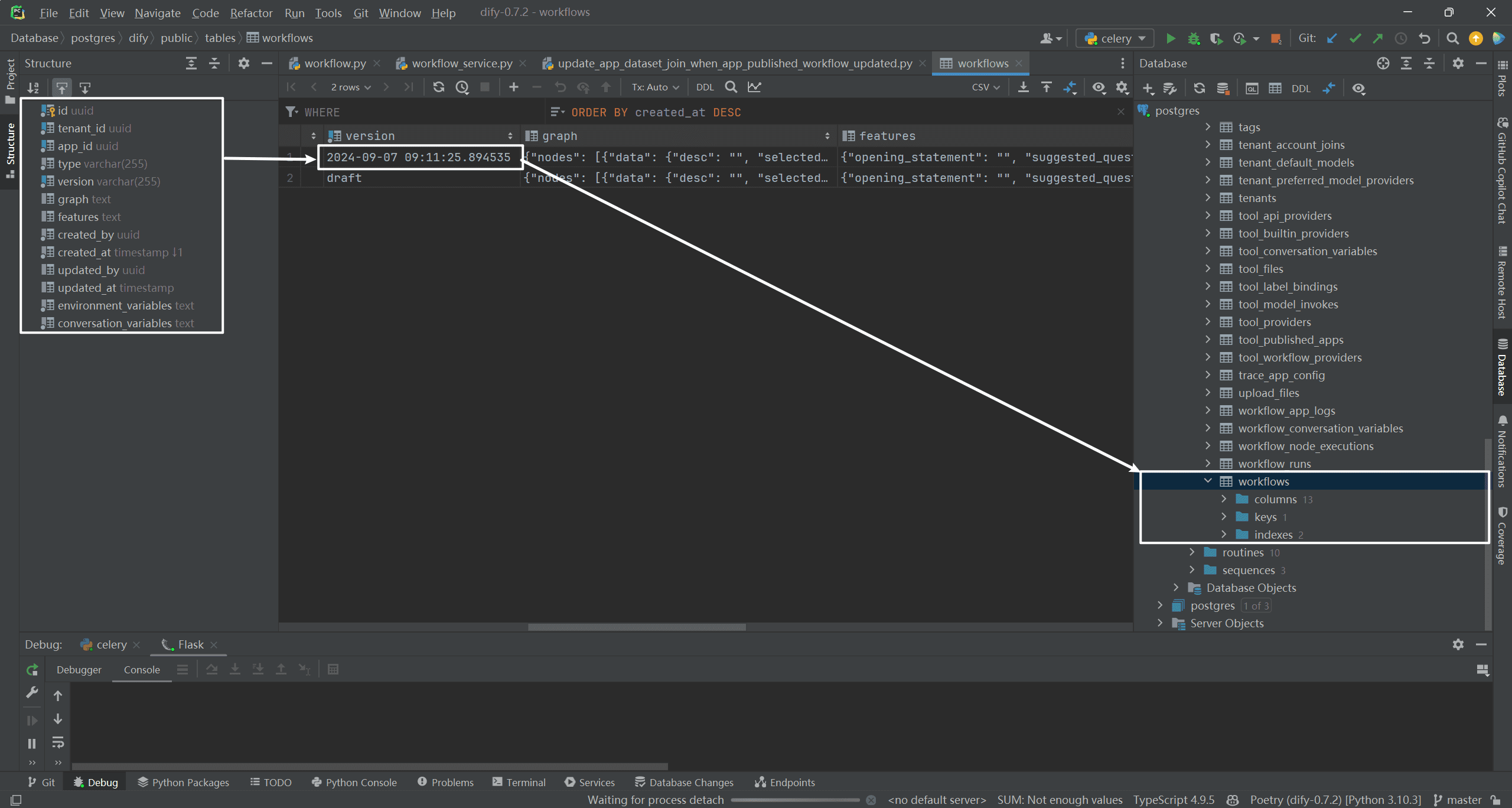
(3) Creating a new workflow record
This mainly consists of creating a new workflow record where the content of the version field is 2024-09-07 09:11:25.894535. indicating that the workflow has been published, not draft (the workflow has not been published and is still being debugged in the workflow canvas). As shown below:
(4) app_published_workflow_was_updated event implementation
@app_published_workflow_was_updated.connect
def handle(sender, **kwargs):
app = sender
published_workflow = kwargs.get("published_workflow")
published_workflow = cast(Workflow, published_workflow)
dataset_ids = get_dataset_ids_from_workflow(published_workflow) # 从工作流中获取数据集ID
app_dataset_joins = db.session.query(AppDatasetJoin).filter(AppDatasetJoin.app_id == app.id).all() # 获取应用数据集关联
removed_dataset_ids = [] # 用于存储移除的数据集ID
if not app_dataset_joins: # 如果没有应用数据集关联
added_dataset_ids = dataset_ids # 添加数据集ID
else: # 如果有应用数据集关联
old_dataset_ids = set() # 用于存储旧的数据集ID
for app_dataset_join in app_dataset_joins: # 遍历应用数据集关联
old_dataset_ids.add(app_dataset_join.dataset_id) # 添加数据集ID
added_dataset_ids = dataset_ids - old_dataset_ids # 添加数据集ID
removed_dataset_ids = old_dataset_ids - dataset_ids # 移除数据集ID
if removed_dataset_ids: # 如果有移除的数据集ID
for dataset_id in removed_dataset_ids: # 遍历移除的数据集ID
db.session.query(AppDatasetJoin).filter(
AppDatasetJoin.app_id == app.id, AppDatasetJoin.dataset_id == dataset_id
).delete() # 删除应用数据集关联
if added_dataset_ids: # 如果有添加的数据集ID
for dataset_id in added_dataset_ids: # 遍历添加的数据集ID
app_dataset_join = AppDatasetJoin(app_id=app.id, dataset_id=dataset_id) # 创建应用数据集关联
db.session.add(app_dataset_join) # 添加应用数据集关联
db.session.commit() # 提交事务
The function of this code is to handle the app_published_workflow_was_updated Signal to update the association relationship between an application and a dataset when the published workflow for that application is updated. The specific steps are as follows:
- Get the application object that sends the signal
appand updated workflow objectspublished_workflowThe - invocations
get_dataset_ids_from_workflowfunction that extracts the dataset ID collection from the updated workflowdataset_idsThe - Query the database to get all the current application's
AppDatasetJoinRecords. - Calculates the dataset IDs to be added and deleted:
- If there are no current
AppDatasetJoinrecords, then all extracted dataset IDs need to be added. - Otherwise, calculate the dataset IDs to be added and deleted.
- If there are no current
- Deleting the need to remove
AppDatasetJoinRecords. - Add new
AppDatasetJoinRecords. - Submit a database transaction.
(5) Role of the AppDatasetJoin table
The AppDatasetJoin table serves to maintain a many-to-many relationship between an application (App) and a dataset (Dataset). Each record represents the association of an application with a dataset. The specific fields are as follows:
- id: primary key that uniquely identifies a record.
- app_id: A unique identifier for the application.
- dataset_id: The unique identifier of the dataset.
- created_at: The timestamp of the record's creation.
- With this table, it is possible to query which datasets are associated with a particular application, or which applications a particular dataset is associated with.
(6) get_dataset_ids_from_workflow() implementation
def get_dataset_ids_from_workflow(published_workflow: Workflow) -> set: # 从工作流中获取数据集ID
dataset_ids = set() # 用于存储数据集ID
graph = published_workflow.graph_dict # 获取工作流图
if not graph: # 如果没有图
return dataset_ids # 返回空集合
nodes = graph.get("nodes", []) # 获取图中的节点
# fetch all knowledge retrieval nodes # 获取所有知识检索节点
knowledge_retrieval_nodes = [
node for node in nodes if node.get("data", {}).get("type") == NodeType.KNOWLEDGE_RETRIEVAL.value
] # 获取所有知识检索节点
if not knowledge_retrieval_nodes: # 如果没有知识检索节点
return dataset_ids # 返回空集合
for node in knowledge_retrieval_nodes: # 遍历知识检索节点
try:
node_data = KnowledgeRetrievalNodeData(**node.get("data", {})) # 获取节点数据
dataset_ids.update(node_data.dataset_ids) # 更新数据集ID
except Exception as e: # 如果出现异常
continue
return dataset_ids
The main function of the get_dataset_ids_from_workflow function is to extract the relevant dataset IDs of all the knowledge retrieval nodes from a given workflow object. the specific steps are as follows:
- Initializes an empty dataset_ids collection for storing dataset IDs.
- Get the graph structure of the workflow graph.
- Returns the empty dataset_ids collection if the graph structure is empty.
- Get all nodes nodes in the graph.
- Filter all nodes of type KNOWLEDGE_RETRIEVAL knowledge_retrieval_nodes.
- Iterate over these knowledge retrieval nodes, extract their dataset IDs and update them in the dataset_ids collection.
- Returns a collection of all extracted dataset IDs.
5. Workflow other interfaces
This part of the interface will not be elaborated, the workflow orchestration conversational application API has been described very clearly.
| serial number | interface name | interface link | Interface Functions Explained |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Send a dialog message | POST /chat-messages | Create session messages that send user input or ask questions. |
| 2 | Uploading files | POST /files/upload | Upload files (currently only images are supported) for use when sending messages. |
| 3 | stop responding | POST /chat-messages/:task_id/stop | Stop streaming responses (only streaming mode is supported). |
| 4 | Message Feedback (Likes) | POST /messages/:message_id/feedbacks | User feedback and likes on messages to facilitate optimization of the output. |
| 5 | Get a list of suggested questions for the next round | GET /messages/{message_id}/suggested | Get a list of suggested questions for the next round. |
| 6 | Get session history messages | GET /messages | Get the history of the session's message logs. |
| 7 | Get session list | GET /conversations | Get a list of the current user's sessions. |
| 8 | Deleting a session | DELETE /conversations/:conversation_id | Deletes the specified session. |
| 9 | session renaming | POST /conversations/:conversation_id/name | Rename the session. |
| 10 | speech-to-text | POST /audio-to-text | Convert voice files to text. |
| 11 | text-to-speech | POST /text-to-audio | Convert text to speech. |
| 12 | Getting Application Configuration Information | GET /parameters | Get configuration information for the application, such as function switches, input parameters, etc. |
| 13 | Getting Application Meta Information | GET /meta | Get the Meta information of the application for getting the tool icon. |
bibliography
[1] Session variables: https://docs.dify.ai/v/zh-hans/guides/workflow/variables[2] Variable assignment: https://docs.dify.ai/v/zh-hans/guides/workflow/node/variable-assignment[3] Variable aggregation: https://docs.dify.ai/v/zh-hans/guides/workflow/node/variable-assigner[4] React Flow Chinese website: https://reactflow-cn.js.org/[5] React Flow English website: https://reactflow.dev/[6] Process implementation of Chatflow create, update, execute and delete operations: https://z0yrmerhgi8.feishu.cn/wiki/FFzxwdF4PijlhjkLUoecOv6Vn8a© Copyright notes
Article copyright AI Sharing Circle All, please do not reproduce without permission.
Related posts

No comments...