Unsloth löst das Problem der doppelten Inferenz in der quantisierten Version von QwQ-32B
Vor kurzem veröffentlichte das Qwen-Team QwQ-32B Modell, ein Inferenzmodell, das in vielen Bereichen verwendet wurde Benchmarks Es ist eine Show, die sich mit der DeepSeek-R1 Die Leistung des Systems ist hervorragend. Allerdings sind viele Benutzer auf unendliche Generierung, übermäßige Duplikate, Token-Probleme und Feinabstimmungsprobleme gestoßen. Dieser Artikel enthält eine ausführliche Anleitung, die Ihnen bei der Fehlersuche und -behebung helfen soll, damit Sie das volle Potenzial des QwQ-32B ausschöpfen können.
Untuch Das vom Team hochgeladene Modell behebt die oben genannten Fehler und ermöglicht eine bessere Unterstützung von Tools und Frameworks wie Fine-Tuning, vLLM und Transformers. Für diejenigen, die Folgendes verwenden lama.cpp Sowie andere Benutzer mit llama.cpp als Backend-Engine, siehe dieser Link Lassen Sie sich beraten, wie Sie das Problem der unendlichen Erzeugung lösen können.
Ungeschliffenes Modell QwQ-32B (Fehler behoben):
- Modell im GGUF-Format
- Dynamische quantitative 4-Bit-Modelle
- BnB 4-bit quantitatives Modell
- 16-Bit-Modell mit voller Präzision
Offiziell empfohlene Einstellungen
⚙️ Offiziell empfohlene Einstellungen
Basierend auf den offiziellen Empfehlungen von Qwen, sind die folgenden Parametereinstellungen für die Modellinferenz empfohlen:
- Temperatur: 0,6
- Top_K: 40 (empfohlener Bereich 20-40)
- Min_P: 0,1 (fakultativ, funktioniert aber gut)
- Top_P: 0,95
- Repetition Penalty: 1.0 (in llama.cpp und Transformers bedeutet 1.0 deaktiviert)
- Chat-Vorlage:
<|im_start|>user\nCreate a Flappy Bird game in Python.<|im_end|>\n<|im_start|>assistant\n<think>\n
llama.cpp Empfohlene Einstellungen
👍 llama.cpp empfohlene Einstellungen
Das Unsloth-Team hat festgestellt, dass viele Benutzer es vorziehen, eine Version größer als 1.0 des Repetition Penalty Dieser Ansatz stört jedoch den Sampling-Mechanismus von llama.cpp. Die Duplikatstrafe sollte die Anzahl der erzeugten Duplikate reduzieren, aber Experimente haben gezeigt, dass dieser Ansatz nicht den gewünschten Effekt hat.
Allerdings ist es auch möglich, die Wiederholungsstrafe ganz zu deaktivieren (auf 1,0 gesetzt). Das Unsloth-Team hat jedoch festgestellt, dass eine angemessene Wiederholungsstrafe immer noch wirksam ist, um die unendliche Erzeugung zu unterdrücken.
Um die Wiederholungsstrafe effektiv nutzen zu können, muss die Reihenfolge der Sampler in llama.cpp angepasst werden, um sicherzustellen, dass bei Anwendung der Repetition Penalty vor der Probenahme, da es sonst zu einer unendlichen Erzeugung kommt. Fügen Sie dazu den folgenden Parameter hinzu:
--samplers "top_k;top_p;min_p;temperature;dry;typ_p;xtc"
Standardmäßig verwendet llama.cpp die folgende Reihenfolge von Samplern:
--samplers "dry;top_k;typ_p;top_p;min_p;xtc;temperature"
Die angepasste Reihenfolge des Unsloth-Teams vertauscht im Wesentlichen die Positionen von Temperatur und Trockenheit und verschiebt min_p nach vorne. Das bedeutet, dass der Probenehmer in der folgenden Reihenfolge angewendet wird:
top_k=40
top_p=0.95
min_p=0.1
temperature=0.6
dry
typ_p
xtc
Wenn das Problem weiterhin besteht, versuchen Sie, die --repeat-penalty Der Wert von 1,0 wurde leicht auf 1,2 oder 1,3 erhöht.
Vielen Dank an @krist486, der uns auf das Problem mit der Abtastrichtung in llama.cpp aufmerksam gemacht hat.
Strafe für trockene Wiederholungen
☀️ Trockene Wiederholung Strafe
Das Unsloth-Team untersuchte die vorgeschlagenen dry penalty Nutzung und versuchte, einen Wert von 0,8 zu verwenden. Die Versuchsergebnisse zeigen jedoch, dass diedry penalty Es ist wahrscheinlicher, dass es zu Syntaxfehlern kommt, insbesondere bei der Codegenerierung. Wenn der Benutzer immer noch auf Probleme stößt, versuchen Sie, die Einstellung dry penalty Erhöhung auf 0,8.
Wenn Sie sich für die Verwendung von dry penaltykann die angepasste Stichprobenreihenfolge ebenso hilfreich sein.
Ollama läuft QwQ-32B Tutorials
🦙 Ollama QwQ-32B Tutorial ausführen
- Falls nicht bereits installiert
ollamaBitte installieren Sie es zuerst!
apt-get update
apt-get install pciutils -y
curl -fSSL [https://ollama.com/install.sh](https://www.google.com/url?sa=E&q=https%3A%2F%2Follama.com%2Finstall.sh) | sh
- Führen Sie das Modell aus! Wenn der Lauf fehlschlägt, versuchen Sie, ihn in einem anderen Terminal auszuführen
ollama serveDas Unsloth-Team hat alle Korrekturen und vorgeschlagenen Parameter (Temperatur usw.) in das Upload-Modell von Hugging Face aufgenommen.paramDokumentation!
ollama run hf.co/unsloth/QwQ-32B-GGUF:Q4_K_M
llama.cpp Tutorial für den Betrieb von QwQ-32B
📖 llama.cpp läuft QwQ-32B Tutorials
- durch (eine Lücke) lama.cpp Holen Sie sich die neueste Version
llama.cpp. Sie können sich auf die folgenden Bauanleitungen beziehen, um zu bauen. Wenn Sie keine GPU haben oder nur CPU-Inferenz durchführen wollen, setzen Sie die-DGGML_CUDA=ONErsetzen durch-DGGML_CUDA=OFF.
apt-get update
apt-get install pciutils build-essential cmake curl libcurl4-openssl-dev -y
git clone [https://github.com/ggerganov/llama.cpp](https://www.google.com/url?sa=E&q=https%3A%2F%2Fgithub.com%2Fggerganov%2Fllama.cpp)
cmake llama.cpp -B llama.cpp/build
-DBUILD_SHARED_LIBS=ON -DGGML_CUDA=ON -DLLAMA_CURL=ON
cmake --build llama.cpp/build --config Release -j --clean-first --target llama-quantize llama-cli llama-gguf-split
cp llama.cpp/build/bin/llama-* llama.cpp
- Laden Sie das Modell herunter (nach der Installation)
pip install huggingface_hub hf_transfer(nach). Q4_K_M oder andere quantisierte Versionen (z. B. BF16 full precision) können ausgewählt werden. Für weitere Versionen besuchen Sie bitte: https://huggingface.co/unsloth/QwQ-32B-GGUF.
# !pip install huggingface_hub hf_transfer
import os
os.environ["HF_HUB_ENABLE_HF_TRANSFER"] = "1"
from huggingface_hub import snapshot_download
snapshot_download(
repo_id="unsloth/QwQ-32B-GGUF",
local_dir="unsloth-QwQ-32B-GGUF",
allow_patterns=[" Q4_K_M "], # For Q4_K_M
)
- Führen Sie das von Unsloth zur Verfügung gestellte Flappy Bird Testskript aus und speichern Sie die Ausgabe in der Datei
Q4_K_M_yes_samplers.txtDokumentation. - Passen Sie die Parameter entsprechend der tatsächlichen Situation an.
--threads 32Legen Sie die Anzahl der CPU-Threads fest.--ctx-size 16384Setzen Sie die Kontextlänge der--n-gpu-layers 99Legen Sie die Anzahl der GPU-Auslastungsebenen fest. Wenn die GPU zu wenig Speicherplatz hat, versuchen Sie, die--n-gpu-layersWert. Entfernen Sie diesen Parameter, wenn nur CPU-Inferenz verwendet wird. --repeat-penalty 1.1im Gesang antworten--dry-multiplier 0.5sind die Parameter für die Wiederholungsstrafe und die Trockenstrafe, die vom Benutzer nach Bedarf angepasst werden können.
./llama.cpp/llama-cli
--model unsloth-QwQ-32B-GGUF/QwQ-32B-Q4_K_M.gguf
--threads 32
--ctx-size 16384
--n-gpu-layers 99
--seed 3407
--prio 2
--temp 0.6
--repeat-penalty 1.1
--dry-multiplier 0.5
--min-p 0.1
--top-k 40
--top-p 0.95
-no-cnv
--samplers "top_k;top_p;min_p;temperature;dry;typ_p;xtc"
--prompt "<|im_start|>user\nCreate a Flappy Bird game in Python. You must include these things:\n1. You must use pygame.\n2. The background color should be randomly chosen and is a light shade. Start with a light blue color.\n3. Pressing SPACE multiple times will accelerate the bird.\n4. The bird's shape should be randomly chosen as a square, circle or triangle. The color should be randomly chosen as a dark color.\n5. Place on the bottom some land colored as dark brown or yellow chosen randomly.\n6. Make a score shown on the top right side. Increment if you pass pipes and don't hit them.\n7. Make randomly spaced pipes with enough space. Color them randomly as dark green or light brown or a dark gray shade.\n8. When you lose, show the best score. Make the text inside the screen. Pressing q or Esc will quit the game. Restarting is pressing SPACE again.\nThe final game should be inside a markdown section in Python. Check your code for errors and fix them before the final markdown section.<|im_end|>\n<|im_start|>assistant\n <think> \n"
2>&1 | tee Q4_K_M_yes_samplers.txt
Die obigen Flappy Bird Spieltipps stammen von Unsloth's DeepSeekR1-Dynamic 1.58bit Blogs. Der vollständige Wortlaut des Stichworts steht unten:
<|im_start|>user
Create a Flappy Bird game in Python. You must include these things:
1. You must use pygame.
2. The background color should be randomly chosen and is a light shade. Start with a light blue color.
3. Pressing SPACE multiple times will accelerate the bird.
4. The bird's shape should be randomly chosen as a square, circle or triangle. The color should be randomly chosen as a dark color.
5. Place on the bottom some land colored as dark brown or yellow chosen randomly.
6. Make a score shown on the top right side. Increment if you pass pipes and don't hit them.
7. Make randomly spaced pipes with enough space. Color them randomly as dark green or light brown or a dark gray shade.
8. When you lose, show the best score. Make the text inside the screen. Pressing q or Esc will quit the game. Restarting is pressing SPACE again.
The final game should be inside a markdown section in Python. Check your code for errors and fix them before the final markdown section.<|im_end|>
<|im_start|>assistant
<think>
Hier sehen Sie den Anfang und das Ende des vom Modell generierten Python-Codes (ohne den Gedankengang):
import pygame
import random
import sys
pygame.init()
### Continues
class Bird:
def __init__(self):
### Continues
def main():
best_score = 0
current_score = 0
game_over = False
pipes = []
first_time = True # Track first game play
# Initial setup
background_color = (173, 216, 230) # Light blue initially
land_color = random.choice(land_colors)
bird = Bird()
while True:
for event in pygame.event.get():
### Continues
if not game_over:
# Update bird and pipes
bird.update()
### Continues
# Drawing
### Continues
pygame.display.flip()
clock.tick(60)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
Das Modell hat erfolgreich ein funktionierendes Flappy Bird-Spiel erzeugt!
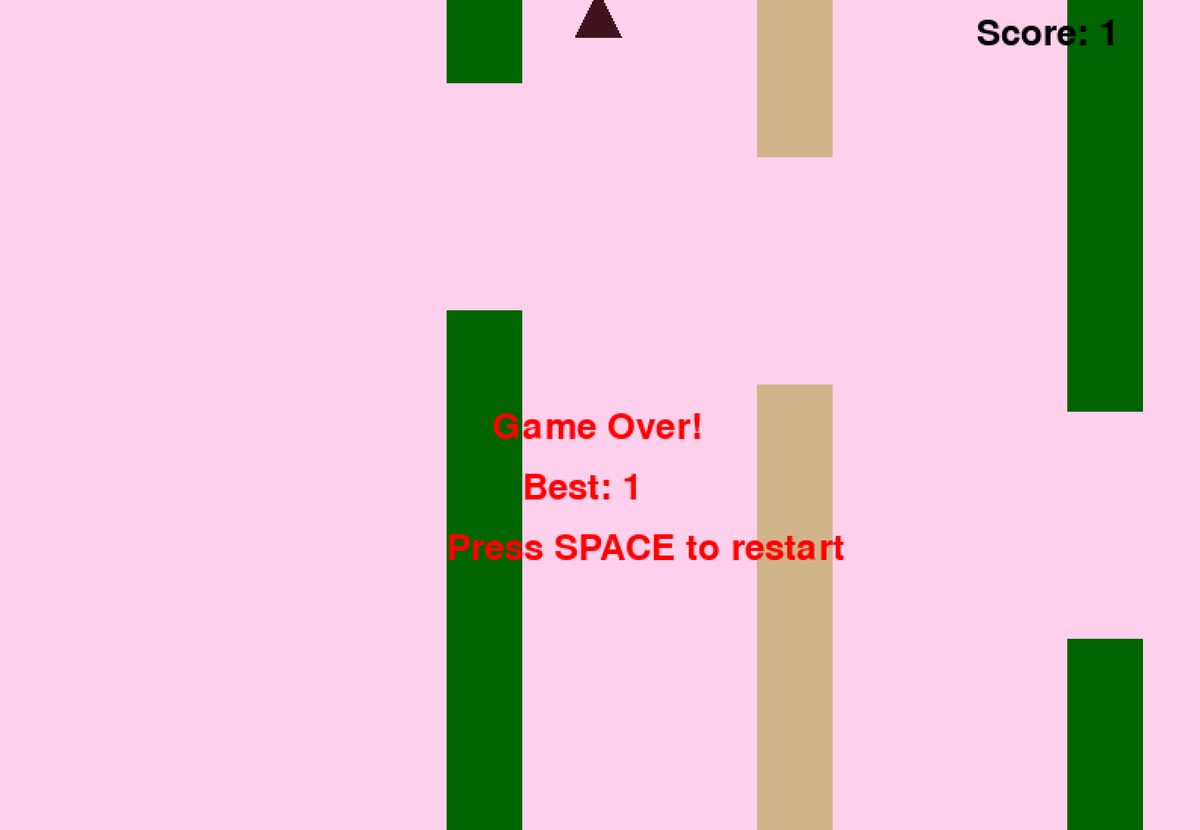
Versuchen Sie als Nächstes, den Parameter --samplers "top_k;top_p;min_p;temperature;dry;typ_p;xtc" zu entfernen, und führen Sie denselben Befehl ohne den Unsloth-Fix aus. Die Ausgabe wird in der Datei Q4_K_M_no_samplers.txt gespeichert.
./llama.cpp/llama-cli
--model unsloth-QwQ-32B-GGUF/QwQ-32B-Q4_K_M.gguf
--threads 32
--ctx-size 16384
--n-gpu-layers 99
--seed 3407
--prio 2
--temp 0.6
--repeat-penalty 1.1
--dry-multiplier 0.5
--min-p 0.1
--top-k 40
--top-p 0.95
-no-cnv
--prompt "<|im_start|>user\nCreate a Flappy Bird game in Python. You must include these things:\n1. You must use pygame.\n2. The background color should be randomly chosen and is a light shade. Start with a light blue color.\n3. Pressing SPACE multiple times will accelerate the bird.\n4. The bird's shape should be randomly chosen as a square, circle or triangle. The color should be randomly chosen as a dark color.\n5. Place on the bottom some land colored as dark brown or yellow chosen randomly.\n6. Make a score shown on the top right side. Increment if you pass pipes and don't hit them.\n7. Make randomly spaced pipes with enough space. Color them randomly as dark green or light brown or a dark gray shade.\n8. When you lose, show the best score. Make the text inside the screen. Pressing q or Esc will quit the game. Restarting is pressing SPACE again.\nThe final game should be inside a markdown section in Python. Check your code for errors and fix them before the final markdown section.<|im_end|>\n<|im_start|>assistant\n<think>\n"
2>&1 | tee Q4_K_M_no_samplers.txt
Ohne Korrekturen erzeugt das Modell Ergebnisse mit Schleifen und einer großen Anzahl von Python-Syntaxfehlern sowie eine Vielzahl anderer Probleme. Der folgende Codeschnipsel zum Beispiel scheint korrekt zu sein, ist aber tatsächlich falsch! Zeile 39 pipes.clear() ### <<< NameError: name 'pipes' is not defined. Haben Sie vergessen 'pipes' zu importieren? Haben Sie vergessen, 'pipes' zu importieren?
import pygame
import random
pygame.init()
# Constants
WIDTH, HEIGHT = 800, 600
GROUND_HEIGHT = 20
GRAVITY = 0.7
PIPE_SPEED = -3
BIRD_SIZE = 45
MIN_GAP = 130
MAX_GAP = 200
PIPE_COLORS = [(0, 96, 0), (205, 133, 63), (89, 97, 107)]
DARK_BROWN = (94, 72, 4)
YELLOW = (252, 228, 6)
screen = pygame.display.set_mode((WIDTH, HEIGHT))
clock = pygame.time.Clock()
def random_light_color():
return (
random.randint(180, 230),
random.randint(190, 300),
random.randint(250, 255)
)
def reset_game():
global bird_x, bird_y
global pipes, score
global background_color, land_color
global bird_shape, bird_color
# Bird properties
bird_x = WIDTH * 0.3
bird_y = HEIGHT // 2
bird_vel = -5 # Initial upward thrust
pipes.clear() ### <<< NameError: name 'pipes' is not defined. Did you forget to import 'pipes'?
Wenn Sie --repeat-penalty weiter auf 1,5 erhöhen, verschlimmert sich die Situation, da die Syntaxfehler deutlicher werden und der Code überhaupt nicht mehr funktioniert.
import pygame
from random import randint # For generating colors/shapes/positions randomly
pygame.init()
# Constants:
WIDTH, HEIGHT =456 ,702 #
BACKGROUND_COLOR_LIGHTS=['lightskyblue']
GAP_SIZE=189 #
BIRD_RADIUS=3.
PIPE_SPEED=- ( ) ?
class Game():
def __init__(self):
self.screen_size=( )
def reset_game_vars():
global current_scor e
# set to zero and other initial states.
# Main game loop:
while running :
for event in pygame.event.get() :
if quit ... etc
pygame.quit()
print("Code is simplified. Due time constraints, full working version requires further implementation.")
Man könnte meinen, dass dies nur ein Problem mit der quantisierten Version von Q4_K_M ist... die Vollpräzisionsversion von BF16 sollte in Ordnung sein, richtig? Dies ist jedoch nicht der Fall. Selbst mit dem BF16-Vollpräzisionsmodell kommt es zu Generierungsfehlern, wenn Sie die vom Unsloth-Team bereitgestellte Korrektur -samplers "top_k;top_p;min_p;temperature;dry;typ_p;xtc" nicht anwenden und die Wiederholungsbestrafung verwenden.
Token nicht angezeigt?
🤔 Token Nicht angezeigt?
Einige Benutzer haben berichtet, dass einige Systeme den Gedankenprozess nicht korrekt ausgeben können, da das Token standardmäßig in die Chat-Vorlage eingefügt wurde. Die Benutzer müssen die Jinja-Vorlage manuell bearbeiten, um es einzuschließen:
{%- if tools %} {{- '<|im_start|>system\n' }} {%- if messages[0]['role'] == 'system' %} {{- messages[0]['content'] }} {%- else %} {{- '' }} {%- endif %} {{- "\n\n# Tools\n\nYou may call one or more functions to assist with the user query.\n\nYou are provided with function signatures within <tools></tools> XML tags:\n<tools>" }} {%- for tool in tools %} {{- "\n" }} {{- tool | tojson }} {%- endfor %} {{- "\n</tools>\n\nFor each function call, return a json object with function name and arguments within <tool_call></tool_call> XML tags:\n<tool_call>\n{\"name\": <function-name>, \"arguments\": <args-json-object>}\n</tool_call><|im_end|>\n" }} {%- else %} {%- if messages[0]['role'] == 'system' %} {{- '<|im_start|>system\n' + messages[0]['content'] + '<|im_end|>\n' }} {%- endif %} {%- endif %} {%- for message in messages %} {%- if (message.role == "user") or (message.role == "system" and not loop.first) %} {{- '<|im_start|>' + message.role + '\n' + message.content + '<|im_end|>' + '\n' }} {%- elif message.role == "assistant" and not message.tool_calls %} {%- set content = message.content.split('</think>')[-1].lstrip('\n') %} {{- '<|im_start|>' + message.role + '\n' + content + '<|im_end|>' + '\n' }} {%- elif message.role == "assistant" %} {%- set content = message.content.split('</think>')[-1].lstrip('\n') %} {{- '<|im_start|>' + message.role }} {%- if message.content %} {{- '\n' + content }} {%- endif %} {%- for tool_call in message.tool_calls %} {%- if tool_call.function is defined %} {%- set tool_call = tool_call.function %} {%- endif %} {{- '\n<tool_call>\n{"name": "' }} {{- tool_call.name }} {{- '", "arguments": ' }} {{- tool_call.arguments | tojson }} {{- '}\n</tool_call>' }} {%- endfor %} {{- '<|im_end|>\n' }} {%- elif message.role == "tool" %} {%- if (loop.index0 == 0) or (messages[loop.index0 - 1].role != "tool") %} {{- '<|im_start|>user' }} {%- endif %} {{- '\n<tool_response>\n' }} {{- message.content }} {{- '\n</tool_response>' }} {%- if loop.last or (messages[loop.index0 + 1].role != "tool") %} {{- '<|im_end|>\n' }} {%- endif %} {%- endif %} {%- endfor %} {%- if add_generation_prompt %} {{- '<|im_start|>assistant\n<think>\n' }} {%- endif %}
Geändert, um das letzte \n zu entfernen. Die Änderung erfordert, dass die Modelle während der Inferenz manuell \n hinzufügen, was jedoch nicht immer funktioniert. Das DeepSeek-Team hat außerdem alle Modelle so geändert, dass sie standardmäßig Token hinzufügen, um das Modell in den Inferenzmodus zu zwingen.
Ändern Sie daher {%- if add_generation_prompt %} {{- 'assistant\n\n' }} {%- endif %} in {%- if add_generation_prompt %} {- 'assistant\n' }} {%- endif %}, d.h. \n entfernen.
Vollständige Jinja-Vorlage, bei der der Teil \n gelöscht wurde.
{%- if tools %} {{- '<|im_start|>system\n' }} {%- if messages[0]['role'] == 'system' %} {{- messages[0]['content'] }} {%- else %} {{- '' }} {%- endif %} {{- "\n\n# Tools\n\nYou may call one or more functions to assist with the user query.\n\nYou are provided with function signatures within <tools></tools> XML tags:\n<tools>" }} {%- for tool in tools %} {{- "\n" }} {{- tool | tojson }} {%- endfor %} {{- "\n</tools>\n\nFor each function call, return a json object with function name and arguments within <tool_call></tool_call> XML tags:\n<tool_call>\n{\"name\": <function-name>, \"arguments\": <args-json-object>}\n</tool_call><|im_end|>\n" }} {%- else %} {%- if messages[0]['role'] == 'system' %} {{- '<|im_start|>system\n' + messages[0]['content'] + '<|im_end|>\n' }} {%- endif %} {%- endif %} {%- for message in messages %} {%- if (message.role == "user") or (message.role == "system" and not loop.first) %} {{- '<|im_start|>' + message.role + '\n' + message.content + '<|im_end|>' + '\n' }} {%- elif message.role == "assistant" and not message.tool_calls %} {%- set content = message.content.split('</think>')[-1].lstrip('\n') %} {{- '<|im_start|>' + message.role + '\n' + content + '<|im_end|>' + '\n' }} {%- elif message.role == "assistant" %} {%- set content = message.content.split('</think>')[-1].lstrip('\n') %} {{- '<|im_start|>' + message.role }} {%- if message.content %} {{- '\n' + content }} {%- endif %} {%- for tool_call in message.tool_calls %} {%- if tool_call.function is defined %} {%- set tool_call = tool_call.function %} {%- endif %} {{- '\n<tool_call>\n{"name": "' }} {{- tool_call.name }} {{- '", "arguments": ' }} {{- tool_call.arguments | tojson }} {{- '}\n</tool_call>' }} {%- endfor %} {{- '<|im_end|>\n' }} {%- elif message.role == "tool" %} {%- if (loop.index0 == 0) or (messages[loop.index0 - 1].role != "tool") %} {{- '<|im_start|>user' }} {%- endif %} {{- '\n<tool_response>\n' }} {{- message.content }} {{- '\n</tool_response>' }} {%- if loop.last or (messages[loop.index0 + 1].role != "tool") %} {{- '<|im_end|>\n' }} {%- endif %} {%- endif %} {%- endfor %} {%- if add_generation_prompt %} {{- '<|im_start|>assistant\n' }} {%- endif %}
Zusätzliche Hinweise
Zusätzliche Hinweise
Das Unsloth-Team vermutete zunächst, dass das Problem auf Folgendes zurückzuführen sein könnte:
- Die Kontextlänge von QwQ beträgt möglicherweise nicht die nativen 128K, sondern 32K plus die YaRN-Erweiterung. Siehe z.B. die Readme-Datei unter https://huggingface.co/Qwen/QwQ-32B:
{
...,
"rope_scaling": {
"factor": 4.0,
"original_max_position_embeddings": 32768,
"type": "yarn"
}
}
Das Unsloth-Team hat versucht, die YaRN-Behandlung in llama.cpp neu zu schreiben, aber das Problem blieb bestehen.
--override-kv qwen2.context_length=int:131072
--override-kv qwen2.rope.scaling.type=str:yarn
--override-kv qwen2.rope.scaling.factor=float:4
--override-kv qwen2.rope.scaling.original_context_length=int:32768
--override-kv qqwen2.rope.scaling.attn_factor=float:1.13862943649292 \
- Das Unsloth-Team vermutete auch, dass der RMS-Layernorm-Epsilon-Wert falsch sein könnte und vielleicht 1e-6 statt 1e-5 betragen sollte. Dieser Link. in rms_norm_eps=1e-06 und Dieser Link. in rms_norm_eps=1e-05. Das Unsloth-Team hat auch versucht, diesen Wert umzuschreiben, aber das Problem ist immer noch nicht gelöst:
--override-kv qwen2.attention.layer_norm_rms_epsilon=float:0.000001 \
- Dank @kalomaze hat das Unsloth-Team auch die Tokeniser-IDs zwischen llama.cpp und Transformers getestet, um zu sehen, ob sie übereinstimmen. Die Ergebnisse zeigen, dass sie übereinstimmen, so dass die Nichtübereinstimmung der Tokeniserkennungen nicht die Ursache des Problems ist.
Hier sind die Ergebnisse des Experiments des Unsloth-Teams:
61KB datei_BF16_keine_sampler.txt
BF16 Volle Präzision, keine Musterreparatur angewendet
55KB datei_BF16_ja_samplers.txt
BF16 Volle Präzision, Stichprobenreparatur angewendet
71KB final_Q4_K_M_keine_Sampler.txt
Q4_K_M Genauigkeit, keine Stichprobenkorrektur angewendet
65KB final_Q4_K_M_yes_samplers.txt
Q4_K_M Genauigkeit, angewandte Stichprobenkorrektur
Tokenizer Fehlerbehebungen
✏️ Tokenizer Fehlerbehebung
- Das Unsloth-Team hat auch einige spezifische Probleme gefunden, die die Feinabstimmung betreffen: Der EOS-Token ist korrekt, aber eine logischere Wahl für den PAD-Token wäre "". Das Unsloth-Team hat die Konfiguration unter https://huggingface.co/unsloth/QwQ-32B/blob/ aktualisiert. Das Unsloth-Team hat die Konfiguration in main/tokenizer_config.json aktualisiert.
"eos_token": "<|im_end|>",
"pad_token": "<|endoftext|>",
Dynamische 4-Bit-Quantisierung
🛠️ Dynamische 4-Bit-Quantisierung
Das Unsloth-Team hat auch ein dynamisches 4-Bit-Quantisierungsmodell hochgeladen, das die Modellgenauigkeit im Vergleich zur einfachen 4-Bit-Quantisierung erheblich verbessert! Die Abbildung unten zeigt die Fehleranalyse der Aktivierungswerte und Gewichte des QwQ-Modells während des Quantisierungsprozesses:

Das Unsloth-Team hat das dynamische 4-Bit-Quantitätsmodell hochgeladen auf: https://huggingface.co/unsloth/QwQ-32B-unsloth-bnb-4bit.
seit vLLM Seit der Version 0.7.3 (20. Februar 2024) https://github.com/vllm-project/vllm/releases/tag/v0.7.3 unterstützt vLLM das Laden von dynamischen 4-Bit-Quantitätsmodellen von Unsloth!
Alle Modelle im GGUF-Format finden Sie unter https://huggingface.co/unsloth/QwQ-32B-GGUF!
© urheberrechtliche Erklärung
Artikel Copyright AI-Austauschkreis Alle, bitte nicht ohne Erlaubnis vervielfältigen.
Ähnliche Artikel

Keine Kommentare...